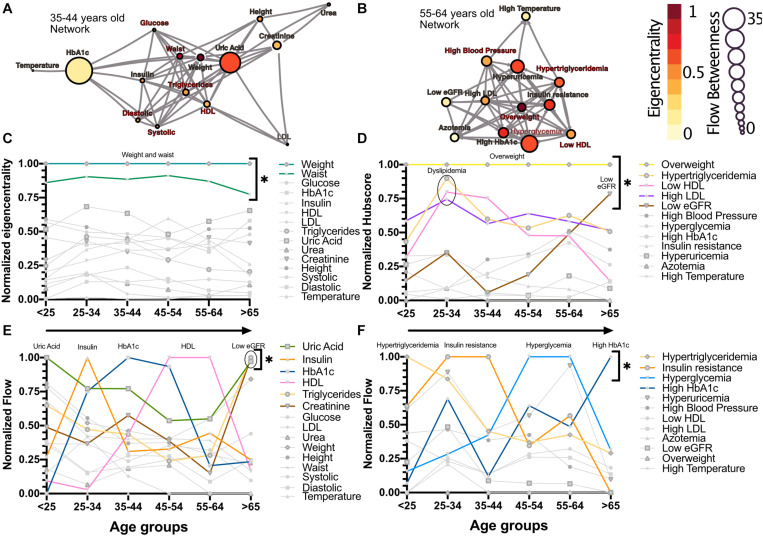
FIGURE 2.
Network modeling highlights physiological and pathological interactions. Centrality measurements identify the role of each physiological variable or pathological state within the metabolic network. (A) Physiological network from 35 to 44 years old, and (B) pathological network from 55 to 64 years old, as examples of the different centrality contribution that each node has. Influence is measured by eigencentrality and is represented by node color, while betweenness is measured by flow and represented by node size. The values from these examples are emphasized inside gray rectangles. (C) Most influential nodes in the physiological variables network, Weight and waist, are indicated. (D) Most influential nodes as seen by eigencentrality in the pathological states network. Overweight, dyslipidemia and low eGFR are indicated. (E) Gatekeeping nodes, as seen by flow betweenness, that mediate the associations between those physiological variables that are not directly connected. (F) Gatekeeping nodes that are the route between unconnected pathological states. The most meaningful nodes in this regard are hypertriglyceridemia, insulin resistance, hyperglycemia and high HbA1c as age increases. * indicates values unlikely to be found by chance alone in CUG tests.