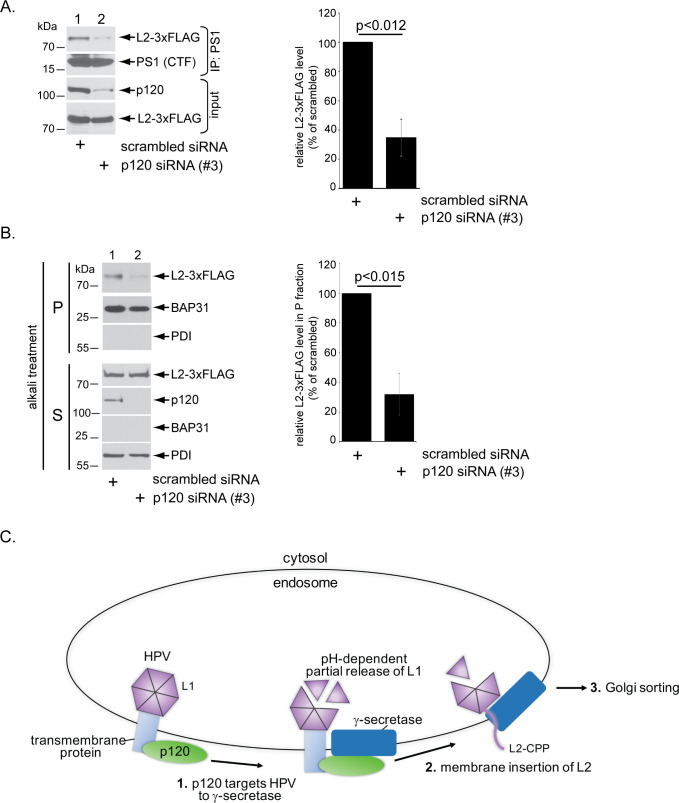
Fig 5. p120 promotes L2 binding to γ-secretase and membrane insertion.
A. HeLa cells transfected with the indicated siRNA were infected with WT HPV16.L2F (Luc) for 16 hrs. Cells were lysed and the resulting extract subjected to immunoprecipitation using an antibody against PS1. The precipitated material was subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting antibodies recognizing the indicated proteins. The level of immunoprecipitated L2-3xFLAG is quantified in the right graph. Data represent the mean ± SD of at least three independent experiments. A two-tailed t test was used to determine statistical significance. B. HeLa cells infected with WT HPV16.L2F (Luc) for 16 hrs were mechanically homogenized and processed to generate a membrane fraction (see Materials and Methods), which was treated with alkali reagents and recentrifuged to generate a pellet fraction (which contains transmembrane proteins) and a supernatant fraction (which harbors soluble proteins). Both fractions were subject to SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with antibodies recognizing the indicated proteins. Presence of the membrane protein BAP31 in the pellet fraction and soluble protein PDI in the supernatant fraction confirm proper fractionation. The level of L2-3xFLAG in the pellet fraction is quantified in the right graph. Data represent the mean ± SD of at least three independent experiments. A two-tailed t test was used to determine statistical significance. C. Proposed model for p120-dependent targeting of HPV16 to γ-secretase. In the endosome, HPV L1 partially dissociates from L2 in a pH-dependent manner. p120 bound to HPV, presumably via a transmembrane protein, targets the virus to γ-secretase (step 1). This is a critical step as γ-secretase promotes insertion of the viral capsid protein L2 into the endosome membrane (step 2). Membrane protrusion mediated by the cell-penetrating peptide (CPP) on the C-terminus of L2 then exposes the retromer binding site to the cytosol, which in turn recruits host factors that direct the virus along an infectious route through the Golgi apparatus and to the nucleus (step 3).