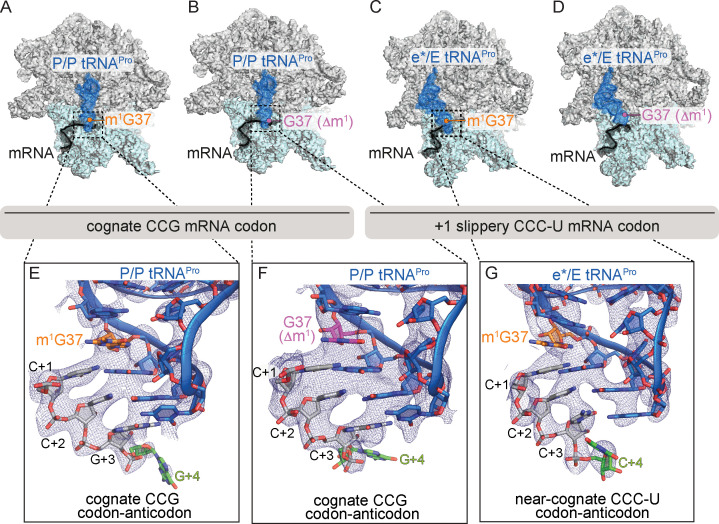
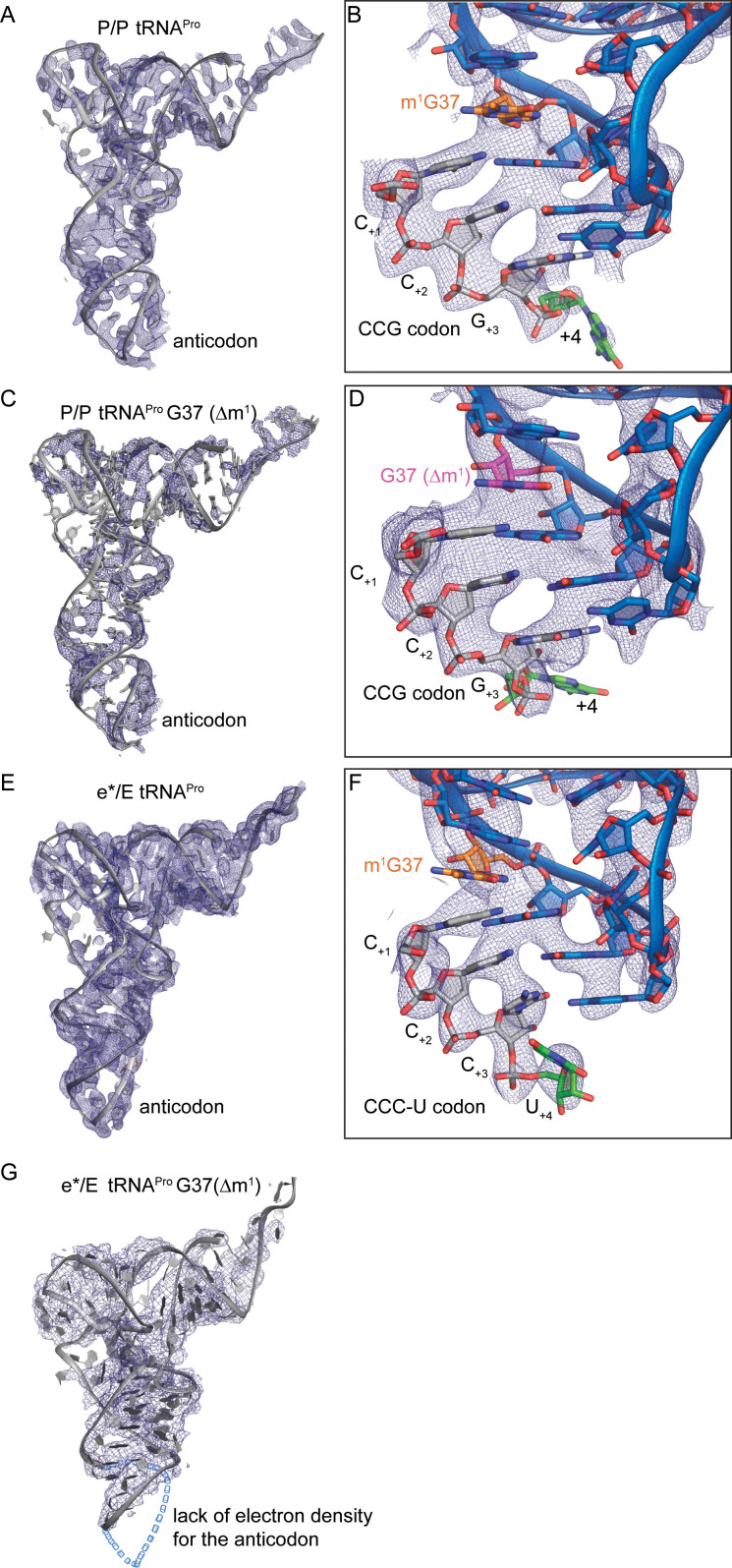
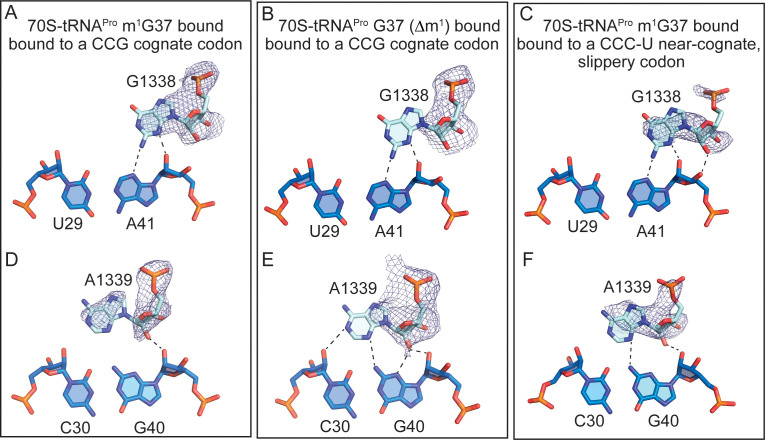
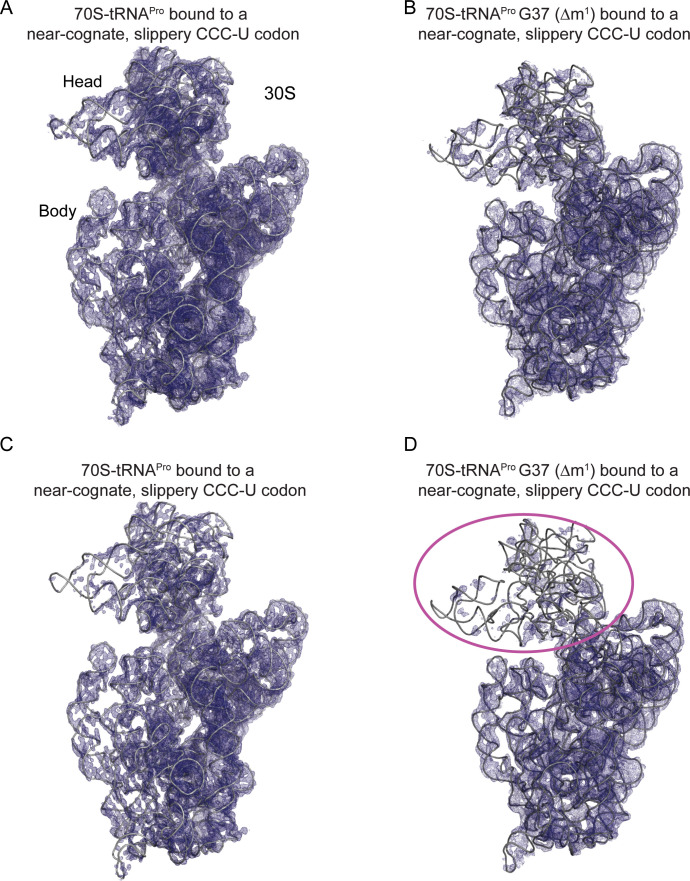
Figure 2. Identity of the mRNA proline codon regulates 30S head domain swivel and tilting.
Overview of 70S ribosome-tRNAPro complex structures: (A) tRNAPro m1G37 on a cognate CCG codon adopts a P/P orientation (located on the P site on the 30S and 50S subunits); (B) tRNAPro lacking the m1G37 modification (G37 Δm1) on a cognate CCG codon also adopts a P/P orientation; (C) tRNAPro on a +1 slippery CCC-U codon adopts an e*/E orientation (e* denotes the location between the E and P sites on the 30S while "E" is the E site of the 50S); and (D) tRNAPro lacking the m1G37 (G37 Δm1) on a +1 slippery CCC-U codon adopts an e*/E orientation. In this complex (panel D), the 30S head domain and anticodon-codon interaction are disordered. In panels A-D, the 16S rRNA of the 30S head domain is removed for clarity. Zoomed-in view of 2Fo-Fc density of (E) the codon–anticodon for tRNAPro on a cognate CCG codon, (F) tRNAPro G37 (Δm1) on a cognate CCG codon in the P site, and (G) tRNAPro G37 (Δm1) on a near-cognate CCC-U codon in position between the E and the P sites (e*). All 2Fo-Fc electron density maps shown in panels E-G are contoured at 1.0σ.