FIG. 1.
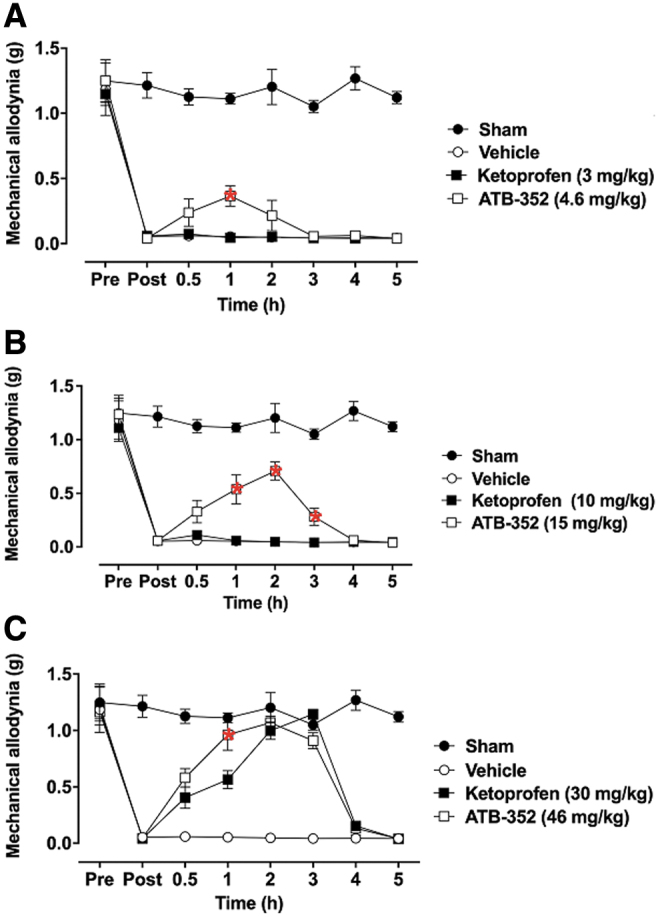
Enhanced analgesic effects of ATB-352 versus ketoprofen on mechanical postoperative allodynia in mice. The presence of mechanical allodynia is indicated by a decrease in the threshold force necessary for the animal response (i.e., paw withdrawal). Mice were orally pretreated with ketoprofen (3, 10, or 30 mg/kg); (A–C), respectively; n = 6, equimolar doses of ATB-352 (4.6, 15, or 46 mg/kg; n = 6), or vehicle (1 mL/kg; n = 6). The control group (sham) did not receive any treatment (n = 6). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM changes in paw withdrawal force thresholds measured before (pre) and 24 h after the incision (post) and then at 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 h after treatment. Red asterisks indicate a significant difference between the mice treated with ATB-352 and the corresponding ketoprofen-treated group (p < 0.05). Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA, followed by the Bonferroni multiple comparison test.
