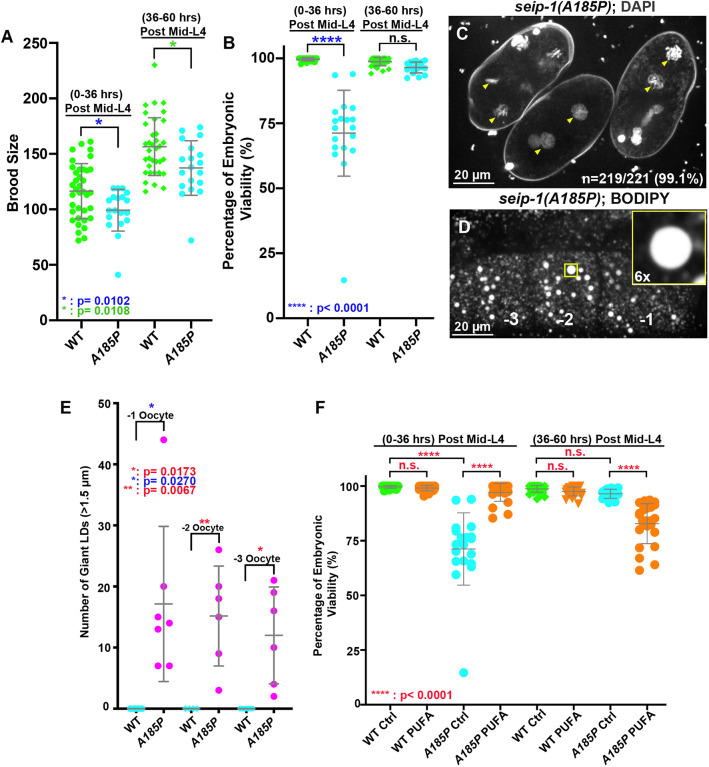
Fig. 7.
A seipin patient-specific allele disrupts eggshell formation and displays enlarged LDs in C. elegans. (A) A conserved patient-specific allele seip-1(A185P) was generated and resulted in reduced brood sizes. (B) seip-1(A185P) causes embryonic lethality in the day 1 (post L4 0-36 h) adult animals. However, embryonic viability of seip-1(A185P) is not affected in the day 2 and 3 (post L4 36-60 h) animals. (C) DAPI staining of zygotic chromatin (yellow arrowheads) in seip-1(A185P) mutant embryos is indicative of a defective permeability barrier. (D) seip-1(A185P) exhibits enlarged LDs in the −1 to −3 oocytes marked by BODIPY. The panel inset shows a 6× enlarged view of a single enlarged LD indicated by the yellow box in the main panel. (E) Quantification of enlarged LDs (diameter >1.5 μm) in −1 to −3 oocytes of seip-1(A185P) animals. (F) The percentage of viable embryos was significantly rescued in the day 1 (post L4 0-36 h) DGLA (PUFA)-fed seip-1(A185P) animals compared with the control. In contrast, the percentage of viable embryos was reduced in the day 2 and 3 animals (post L4 36-60 h) fed with PUFAs. Data are mean±s.d. Statistical significance was determined using an unpaired two-tailed Student's t-test. n.s., not significant.