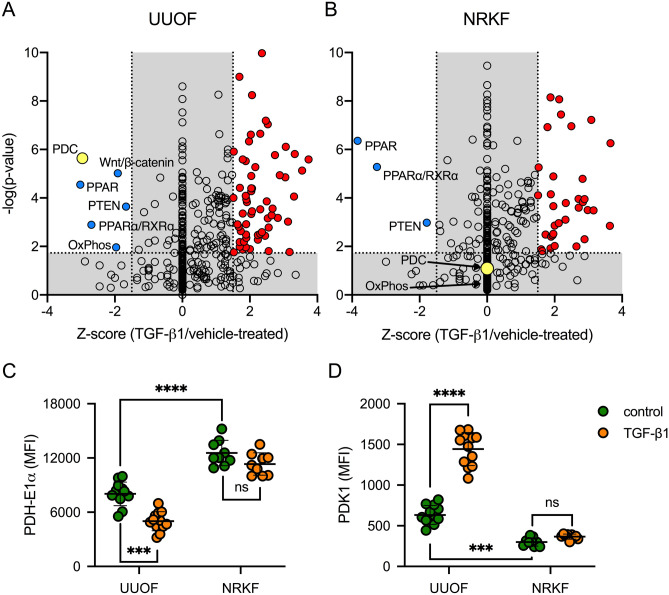
Figure 1.
Divergent effects of TGF-β1 on PDC transcription in injury-primed and normal renal kidney fibroblasts. (A, B) Ingenuity pathway analysis (IPA) was used to predict the activation state of canonical pathways activated or inhibited by 24-h treatment with 1 ng/mL TGF- β1 compared to vehicle (PBS) in (A) UUOF or (B) NRKF. IPA uses a literature-based database of known interactions between transcriptional regulators and their target genes to define an expected expression pattern of targets within each pathway for activated (Z-score ≥ 2) or inhibited (Z-score ≤ − 2) states. The P-value provides a measure of how likely the observed association between a specific pathway and each dataset would be if due to chance alone. Adjusted P-value < 0.05 (− log10 = 1.3) were considered significant. Canonical pathways predicted to be activated by TGF-β1 are shown in red, inhibited pathways are coloured blue with the remainder depicted as open circles. The acetyl-CoA biosynthesis (PDC) pathway is highlighted in yellow. (C, D) Quantitative flow cytometric analysis of TGF-β1-induced changes in (C) PDH-E1α and (D) PDK1 staining (mean fluorescence intensity, MFI) in UUOF and NRKF after 24 h treatment (pooled data from 3 independent experiments). Plots show mean ± SEM. ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001; ns, not significant. P-values were determined in (C, D) using two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test.