Figure 7.
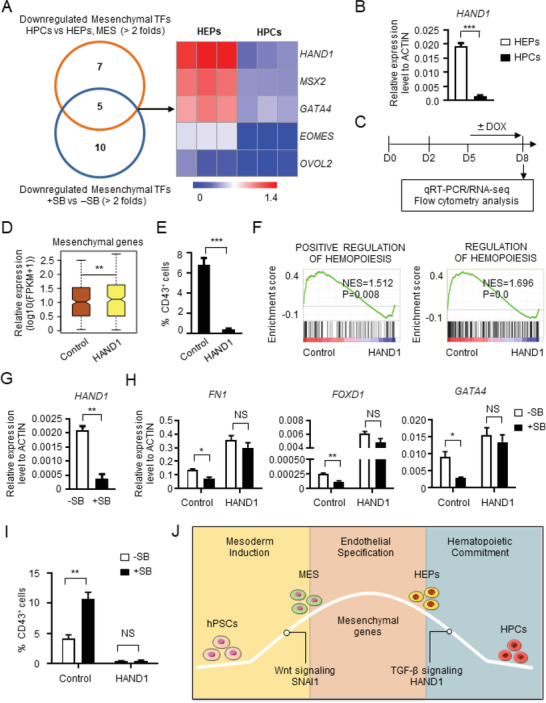
HAND1 mediates the suppressive function of TGF‐β signaling in EHT. A) The screening strategy for identifying potential mesenchymal genes regulating the transition from HEPs to HPCs. B) The relative expression level of HAND1 between HEPs and HPCs. C) The strategy of assessing the expression of mesenchymal genes and the hematopoietic potential with or without HAND1 overexpression. D) The box plot showing the expression level of mesenchymal genes in the CD31+ cells with or without HAND1 overexpression. E) The percentage of CD43+ HPCs with or without HAND1 overexpression detected by flow cytometry. F) Comparison of “Positive regulation of hemotopoiesis” and “Regulation of hemotopoiesis” in the CD31+ cells with or without HAND1 overexpression. G) The relative expression level of HAND1 in the CD31+ cells with or without SB431542 (SB) treatment detected with real‐time PCR. H) The relative expression level of representative mesenchymal genes in the CD31+ cells derived from Control and HAND1 overexpressed hESCs with or without SB treatment detected with real‐time PCR. I) The percentage of CD43+ HPCs derived from Control and HAND1 overexpressed hESCs with or without SB treatment analyzed with flow cytometry. J) A working model for the expression pattern, regulation and function of mesenchymal genes during hematopoietic differentiation of hPSCs. NS, not significant, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001.
