Figure 6.
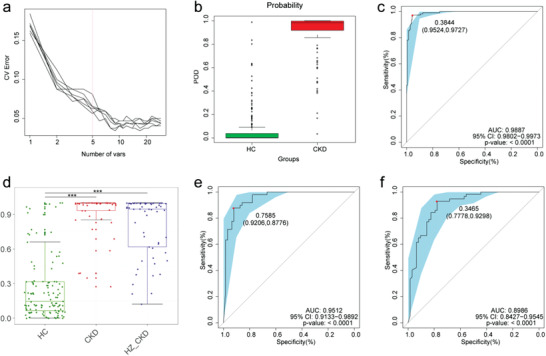
Diagnostic potential of gut microbial markers in CKD patients. a) Five microbial markers were selected as the optimal markers set by the random forest model. b) The POD value was significantly increased in CKD (n = 110) versus HC (n = 210) in the discovery cohort. c) The POD index achieved an AUC value of 0.9887 with 95% CI of 0.9802 to 0.9973 between CKD (n = 110) versus HC (n = 210) in the discovery cohort (p < 0.0001). d) The POD values were remarkably increased in CKD (n = 49) and HZ_CKD (n = 57) compared with HC (all p < 0.001). e) The POD index achieved an AUC value of 0.9512 with 95% CI of 0.9133 to 0.9892 between CKD (n = 49) versus HC (n = 63) in the validation cohort (p < 0.0001). f) The POD index achieved an AUC value of 0.8986 with 95% CI of 0.8427 to 0.9545 between HZ_CKD (n = 57) versus HC (n = 63) in the independent diagnostic cohort (p < 0.0001). *, p < 0.05, **, p < 0.01, ***, p < 0.001. CV Error, the cross‐validation error; CKD, chronic kidney disease; HZ_CKD, the patients of CKD come from Hangzhou; HC, healthy controls; POD, probability of disease; CI, confidence interval; AUC, area under the curve.
