Figure 1.
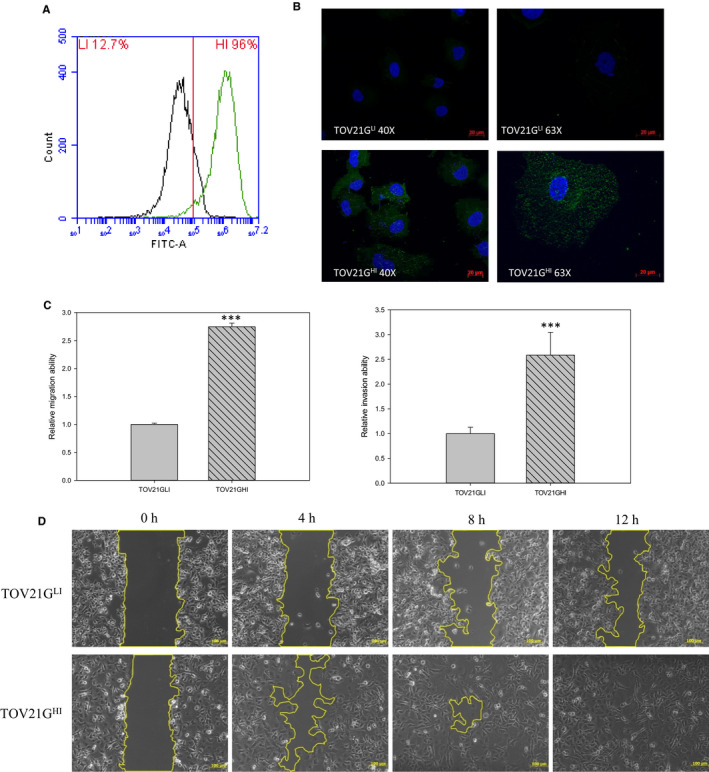
Isolation of highly invasive ovarian cancer cells according to the expression level of Globo H. GH‐specific antibody Mbr‐1 was used to detect GH expression in TOV21GLI/TOV21GHI cells via flow cytometry and immunofluorescence (IF). A, Cells were treated with anti‐Globo H antibody followed by the FITC‐conjugated secondary antibody. Stained cells were analysed by flow cytometry by detecting FITC signal. B, TOV21GLI and TOV21GHI cells were incubated with anti‐Globo H antibody followed by FITC‐conjugated secondary antibody. DAPI was used for nuclear staining. The representative images are displayed at 40× and 63× magnification using fluorescence microscopy. C, Right panel: transwell invasion assay with matrigel pre‐coated condition was utilized to measure the invasive ability of TOV21GLI and TOV21GHI cells. Left panel: transwell migration assay was used for monitoring migration ability of TOV21GLI and TOV21GHI cells. The migration and invasion abilities were quantified by dissolving the cells stained with crystal violet on the underside of the membrane. Absorbance values were normalized to the corresponding value of TOV21GLI cells. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM. of n = 3 measurements. *, P < .05; **, P < .01; ***, P < .001. D, Wound healing of TOV21GLI and TOV21GHI cells was monitored and photographed at 0, 4, 8 and 12 h by using an optical microscope
