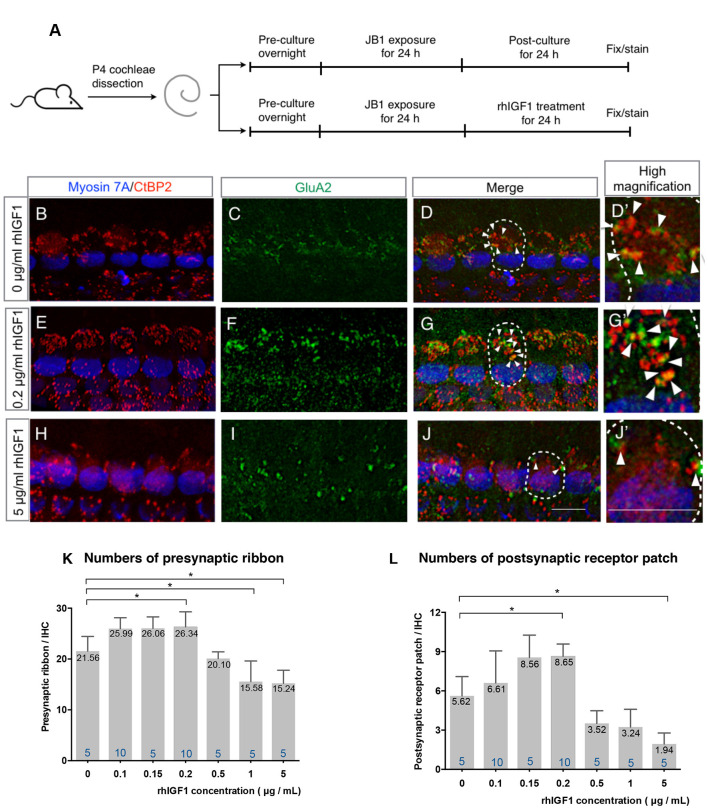
Figure 3.
Effect of exogenous IGF1 on the recovery of ribbon synapses. Cochlear explants from P4 mice were exposed to 50 μg/ml JB1 for 24 h, after which they were incubated with culture media supplemented with rhIGF1 at a concentration of 0.1, 0.15, 0.2, 0.5, or 1, 5 μg/ml for 24 h (A). (B–D) Maximal-intensity projection images with z-stack of the immunostaining images of specimens cultured without rhIGF1. Panels (E–J) are maximal-intensity projection images of the recovery of ribbon synapses in specimens cultured with 50 μg/ml JB1 for 24 h, followed by rhIGF1 treatment for 24 h at concentrations of 0.2 and 5 μg/ml, respectively. Arrows show the postsynaptic receptor patches and dotted lines indicate the location of an IHC. Exogenous rhIGF1 showed significant effects on the number of both presynaptic ribbons (K; p < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA) and postsynaptic receptor patches (L; p < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA). Tukey’s post hoc test revealed significant difference at concentrations of 0.2 (p = 0.034), 1 (p = 0.017), and 5 μg/ml (p = 0.010) in the number of presynaptic ribbons, and at concentrations of 0.2 (p = 0.020) and 5 μg/ml (p = 0.012) in the number of postsynaptic receptor patches, in comparison with controls which were cultured in 0 μg/ml rhIGF1. Scale bars: 10 μm. Data are expressed as mean (digits at the top of each bar) ± SD. The digits at the bottom of each bar represent the sample number. *p < 0.05 by one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. P4, postnatal day 4; IHC, inner hair cell; SD, standard deviation; rhIGF1, recombinant human insulin-like growth factor-1; ANOVA, analysis of variance.