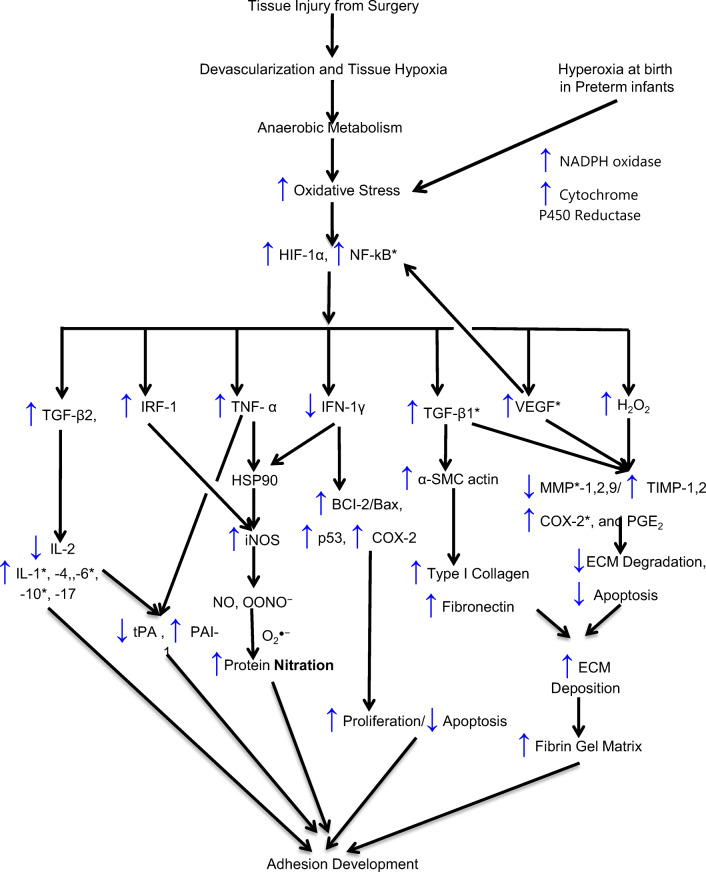
Fig. 2.
Proposed chain of events; growth factors, cytokines, associated gene mutations, and SNPs involved in adhesion development. ↑ denotes an increase and ↓ a decrease; BCl-2, B cell CLL/lymphoma 2; BAX, BCl2-associated X; COX-2, cyclooxygenase 2; ECM, extracellular matrix; HO, hydroxyl radical; H2O2, hydrogen peroxide; HIF, hypoxia-induced factor; HSP90, heat shock protein 90; IFN-γ, interferon-gamma; IL, interleukin; iNOS, inducible nitrous oxide synthase; IRF-1, interferon regulatory factor-1; MMP, matrix metalloproteinases; NADP, nicotine adenine dinucleotide phosphate; NF-kB, nuclear factor-kB; NO, nitric oxide; NOS, nitric oxide synthase; O2•−, superoxide; ONOO−, peroxynitrite; P53, tumor protein 53; PAI-1, plasminogen activator inhibitor; PGE2, prostaglandin E2; TGF-β1, transforming growth-beta1; TIMP, tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor; tPA, tissue plasminogen activator; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor