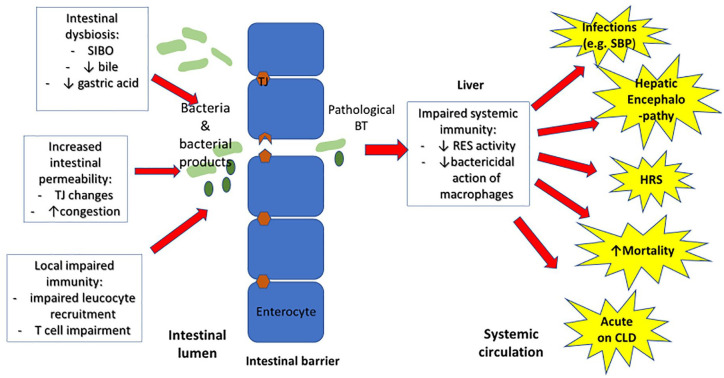
Figure 2.
Mechanisms and consequences of BT in liver disease: changes to the intestinal microbiota, intestinal permeability and local immune responses lead to increased BT. In combination with reduced systemic immunity in the liver (reduced RES and macrophage activity), these changes may lead to complications of liver disease including increased infections such as SBP, acute decompensation of cirrhosis, HRS, HE and increased mortality.
BT, bacterial translocation; CLD, chronic liver disease; HE, hepatic encephalopathy; HRS, hepatorenal syndrome; RES, reticuloendothelial system; SBP, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis; SIBO, small intestinal bacterial overgrowth.