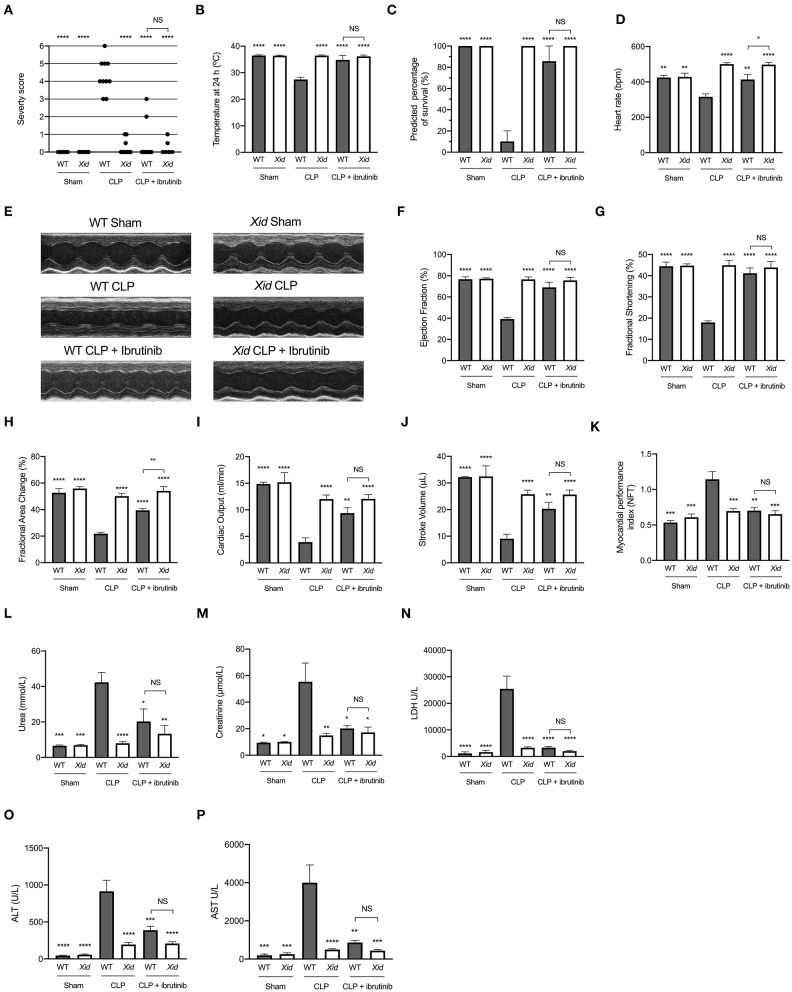
Figure 1.
Xid mice are protected from sepsis-induced multiple organ failure. WT and Xid mice were randomly selected to undergo sham or CLP surgery, 1 h later ibrutinib (30 mg/kg) was administered intravenously. At 24 h after CLP, cardiac function was assessed by echocardiography and parameters of renal and liver function were assessed in serum. (A) Severity Score 24 h after CLP. (B) Temperature 24 h after CLP (°C). (C) Predicted percentage of survival (%). (D) Heart rate 24 h after CLP (bmp). (E) Representative m-mode images. (F) Ejection Fraction (%). (G) Fractional shortening (%). (H) Fractional area change (%). (I) Cardiac output (ml/min). (J) Stroke volume (μL). (K) Myocardial performance index (NFT). (L) Urea (mmol/L). (M) Creatinine (μmol/L). (N) Lactate dehydrogenase (U/L). (O) ATL (U/L). (P) AST (U/L). The following groups were studied WT sham (n = 5), Xid sham (n = 5), WT-CLP (n = 10), Xid-CLP (n = 10), WT-CLP + ibrutinib (n = 8), and Xid-CLP + ibrutinib (n = 6). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM and analyzed by one-way ANOVA with a Bonferroni post hoc-test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001 vs. WT-CLP.