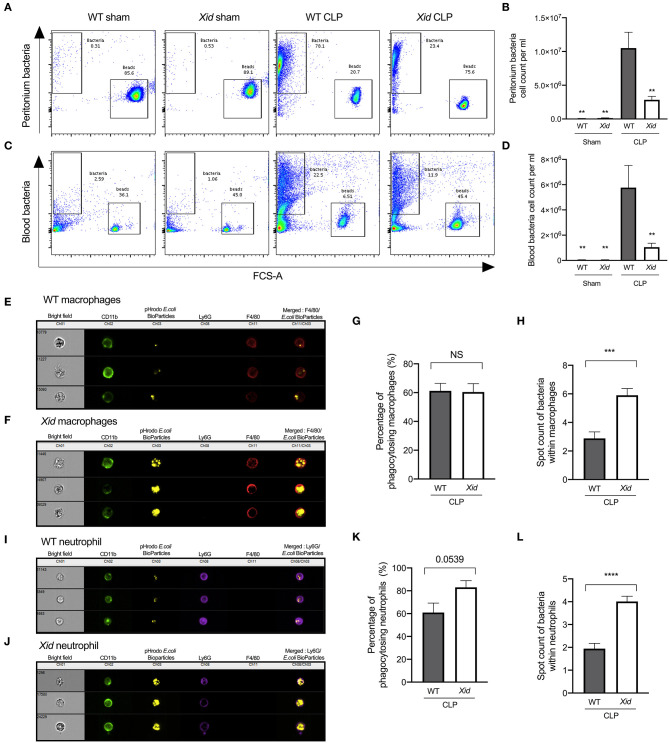
Figure 4.
Xid mice result in enhanced bacterial clearance in peritoneum and blood due to increased phagocytosis in sepsis. Mice underwent sham or CLP surgery, 24 h later peritoneal lavage fluid and blood were analyzed. Macrophages identified as (CD11b+, F4/80+, and Ly6G−) and neutrophils identified as (CD11b+, F4/80−, and Ly6G+). (A) Representative images of peritoneal bacteria cell count. (B) Peritoneum bacteria cell count per ml. (C) Representative images of blood bacteria cell count. (D) Blood bacteria cell count per ml. (E) Representative images of WT-CLP macrophages phagocytosis on the imagestream. (F) Representative images of Xid-CLP macrophages phagocytosis on the imagestream. (G) Percentage of phagocytosing macrophages (%). (H) Average number of pHrodo red E. coli BioParticles within macrophages. (I) Representative images of WT-CLP neutrophil phagocytosis on the imagestream. (J) Representative images of Xid-CLP neutrophil phagocytosis on the imagestream. (K) Percentage of phagocytosing neutrophils (%). (L) Average number of pHrodo red E. coli BioParticles within neutrophils. The following groups were studied WT sham (n = 5), Xid sham (n = 5,) WT-CLP (n = 10), and Xid-CLP (n = 10). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM and analyzed by one-way ANOVA with a Bonferroni post hoc-test or a two-tailed Students t-test as appropriate. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001 vs. WT-CLP.