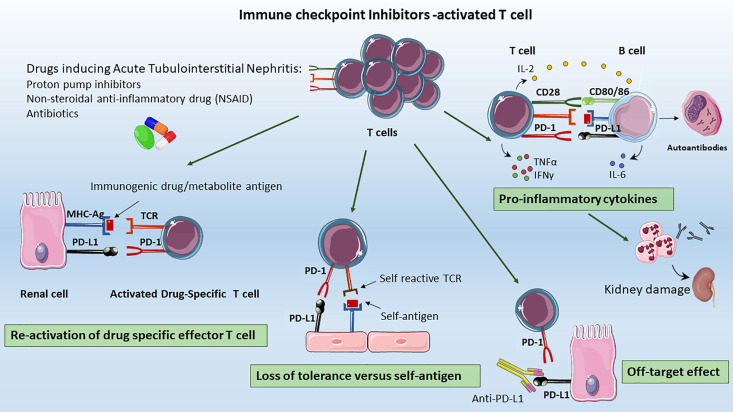
Figure 2.
Mechanisms of ICIs-associated AKI. The proposed mechanisms underlying ICIs-induced AKI include: Re-activation of drug specific T cells: T cell primed by different drugs (e.g. previous or concomitant antibiotics, PPIs, or NSAIDs) became latent over the time; however they can be re-activated by ICIs, leading to loss of tolerance; Loss of tolerance versus self-antigens: the formation, the selection and proliferation of a clone of self-reactive T-cells, the auto-reactive T cell could activated self-reactive B cells leading to auto-antibody release, that to renal injury; Off Target Effect: the upregulation of PD-L1 on renal tubular epithelial cells can lead to kidney damage by effector T lymphocytes infiltration resulting in acute tubulointerstitial nephritis, Pro-inflammatory cytokines: ICIs promote the migration and activation of effector T cells in renal tissue, the infiltration of other immune cells as B cells together with pro-inflammatory cytokines release as CXCL10, TNFα, IL-6 that contribute to the generation of an inflammatory milieu, leading to renal damage.