Figure 4.
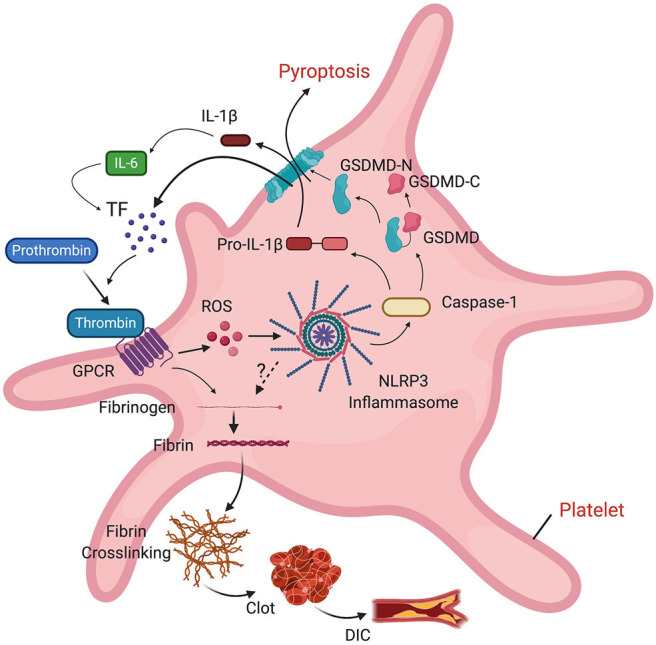
Role of the inflammasome on clot formation. Thrombin binds to a GPCR in platelets, resulting in ROS-dependent activation of the inflammasome and release of IL-1β into the cell. IL-1β stimulates production of IL-6. IL-6 stimulates tissue factor (TF) to convert prothrombin into thrombin. TF-containing microvesicles are released by pyroptosis following inflammasome activation. Thrombin then converts fibrinogen into fibrin, leading to fibrin cross-linking, clot formation and DIC.
