Fig. 1.
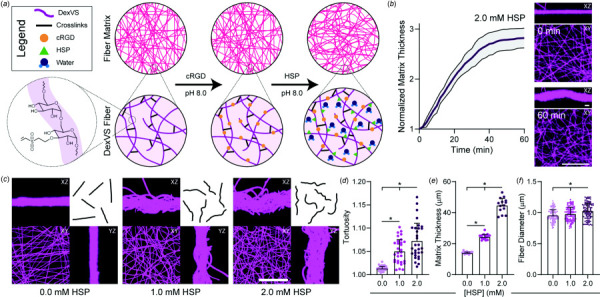
Functionalization of hydrogel fibers with HSP induces crimp in DexVS matrices. (a) Schematic representation of DexVS fibers with controlled adhesive ligand and crimping via functionalization with the cell adhesive peptide cRGD and hydrophilic swelling peptide (HSP, peptide sequence: CGRDGS), respectively. (b) Matrix thickness quantified over time immediately after adding 2.0 mM HSP (n = 6 matrices). (c) Confocal fluorescent images and orthogonal maximum intensity projections of DexVS matrices functionalized with variable HSP concentrations with representative fiber outlines. Scale bar: 50 μm. Quantification of (d) fiber tortuosity (n = 30 fibers), (e) matrix thickness (n = 14 matrices), and (f) fiber diameter (n = 100 fibers) as a function of HSP concentration. All data presented as mean±standard deviation; *p < 0.05.
