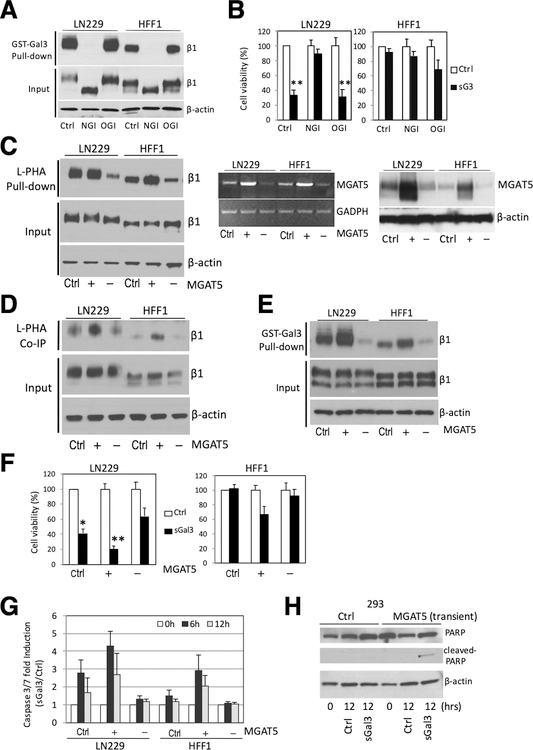
Figure 6. Alteration in MGAT5 expression effects complex N-glycan formation on β1 integrin, sGal-3-β1 integrin interaction and sGal-3-mediated cell killing.
A) GST-Gal-3 pull-down assay showing that kifunensine (100 μM), an α-mannosidase inhibitor that blocks N-glycan processing (NGI), abrogated GST-Gal-3-β1 integrin interaction. Loss of N-glycans reduces size of β1 integrin (see input). Treatment with benzyl-N-acetyl-α-D-galactosamide (α-benzyl-GalNAc) (2 mM), an O-glycosylation inhibitor (OGI) had no effect.
B) Crystal violet cell viability assay showing kifunensine pre-treatment (24 hrs) prevented sGal-3-mediated cell death in LN229 cells. Cells were pre-treated with NGI or OGI for 24 hrs, then 1x control or sGal-3 CM was added and cells incubated for another 72 hrs. N=3 (in triplicates). **p<0.01 (unpaired t-test)
C) L-PHA pulldown assay shows MGAT5 overexpression (+) increases, while MGAT5 knockdown (–) decreases L-PHA binding to β1 integrin. Cells were transiently transfected with control plasmid (Ctrl.) or expression vectors for MGAT5 (+) or shRNA for MGAT5 (–) and cell extracts analyzed after 48 hrs. L-PHA-agarose beads were used to specifically pull-down proteins carrying N-glycan branches synthesized by MGAT5, followed by Western blot for β1 integrin (left panel). RT-PCR analysis (middle panel) and Western blot (right panel) show increase/decrease in MGAT5 mRNA/protein levels.
D) Co-immunoprecipitation experiments showing increased/decreased binding of L-PHA to cell surface β1 integrins with overexpression (+) or knockdown (–) of MGAT5. Cells were transiently transfected as in C), then incubated with purified L-PHA (2.5 μg/ml) for 2 hrs at RT and cell extracts prepared. Cell surface proteins bound to L-PHA were then immunoprecipitated with anti-L-PHA antibodies (2.5 μg/ml) and protein G agarose beads followed by β1 integrin western blot. (Ctrl., +, -) as above.
E) GST-Gal-3 pulldown assay shows that alteration in MGAT5 expression modulates Gal-3 interaction with β1 integrin. Cells were transiently transfected as in C), then cell extracts were incubated with GST-Gal-3 beads and bound β1 integrin detected by Western blot. (Ctrl., +, -) as above.
F) Crystal violet cell viability assay showing modulation of MGAT5 expression alters cell sensitivity to sGal-3-mediated killing. Note that increased MGAT5 expression sensitizes HFF-1 cells to sGal-3 killing. Cells were transiently transfected as in C), then treated with sGal-3 CM for 72 hrs. N=triplicates; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 (unpaired t-test).
G) GLO assay showing modulation of MGAT5 expression alters the cell sensitivity to sGal3-induced apoptosis. Cells were transiently transfected as in C), then treated with sGal-3 for 6 to 12 hrs and caspase-3/7 activation measured. Note that increased MGAT5 expression sensitizes HFF-1 cells to sGal3-induced caspase 3/7 activation, while MGAT5 knockdown reduces cell death in LN229 cells. Fold induction is based on ratio of sGal-3/control luciferase units. Fold ratio at 0 hr is 1. (n = 2).
H) Western blot showing that transient transfection of MGAT5 renders 293 cells susceptible to sGal-3-mediated PARP cleavage.