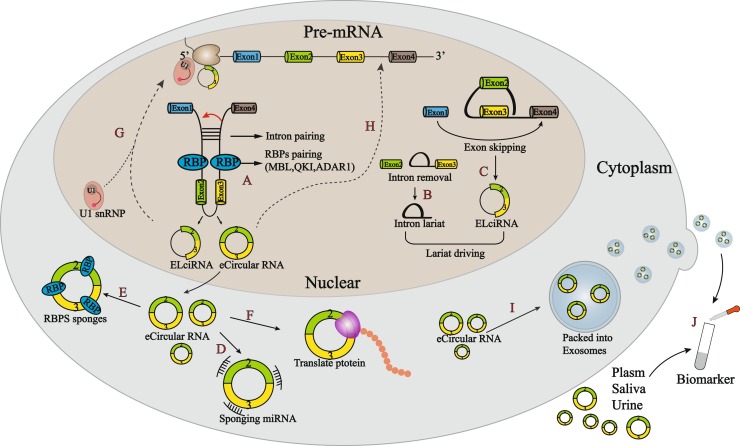
Fig. 1.
Formation and function of circRNAs. (A) The cis-acting elements and trans-acting factors participate in circularization. The cis-acting element allows the introns flanking exons directly base pair into circularization through SINEs. Trans-acting factor driving circularization by binding to specific sites of introns flanking exons. Among them, MBL and QKI promote cyclization, while ADAR1 inhibits circRNAs formation. (B, C) Lariat-driven circularization mode includes exon skipping and intron removal toform EIciRNAs and ciRNAs respectively. (D) CircRNAs act as miRNA sponges to inhibit the interaction between miRNAs and their target mRNAs. (E) Circ RNAs directly bind RBPs to affect gene expression. (F) CircRNAs directly bind RBPs to affect gene expression. (G) CircRNAs interact with U1 snRNP to form circRNAs-U1 snRNP complexes and regulate gene transcription in the nucleus. (H) RNA-DNA hybrid strand regulates its parental DNA transcription by a negative feedback loop. (I) CircRNAs are packed into exosomes and involved in cell-to-cell signal transmission. (J) Some circRNAs exists freely in various body fluids such as blood, saliva, and urine, together with exosomes circuRNAs can be used as biomarkers for disease diagnosis.