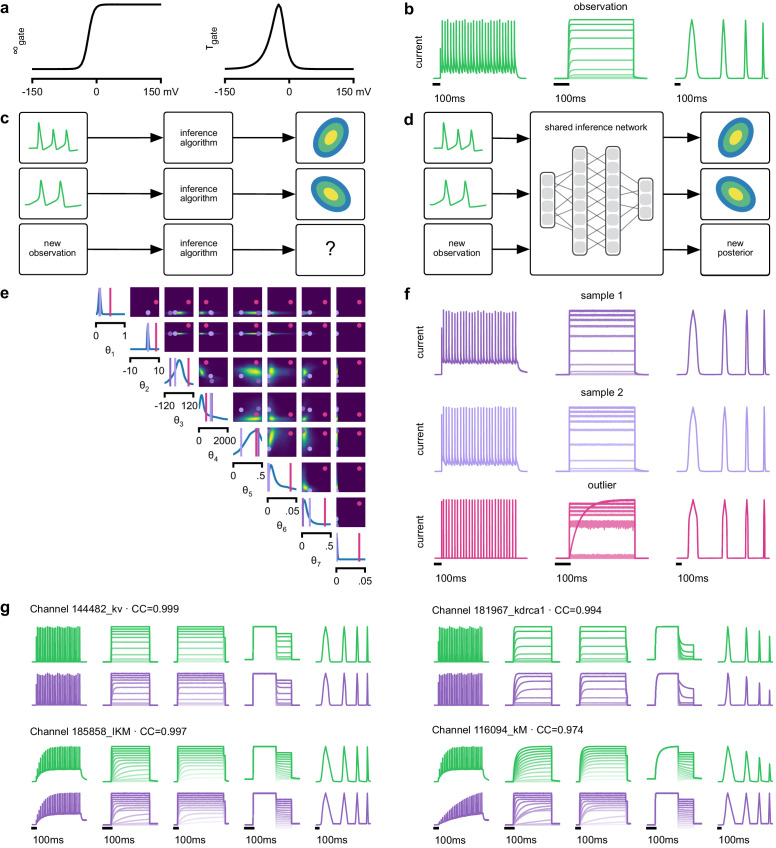
Figure 3. Inference on a database of ion-channel models.
(a) We perform inference over the parameters of non-inactivating potassium channel models. Channel kinetics are described by steady-state activation curves, , and time-constant curves, . (b) Observation generated from a channel model from ICG database: normalized current responses to three (out of five) voltage-clamp protocols (action potentials, activation, and ramping). Details in Podlaski et al., 2017. (c) Classical approach to parameter identification: inference is optimized on each datum separately, requiring new computations for each new datum. (d) Amortized inference: an inference network is learned which can be applied to multiple data, enabling rapid inference on new data. (e) Posterior distribution over eight model parameters, to . Ground truth parameters in green, high-probability parameters in purple, low-probability parameters in magenta. (f) Traces obtained by sampling from the posterior in (e). Purple: traces sampled from posterior, that is, with high posterior probability. Magenta: trace from parameters with low probability. (g) Observations (green) and traces generated by posterior samples (purple) for four models from the database.