Extended Data Fig. 7. E. coli BW25113 exposed to SMX drug stress reduce colitis severity in an IL-10-dependent manner.
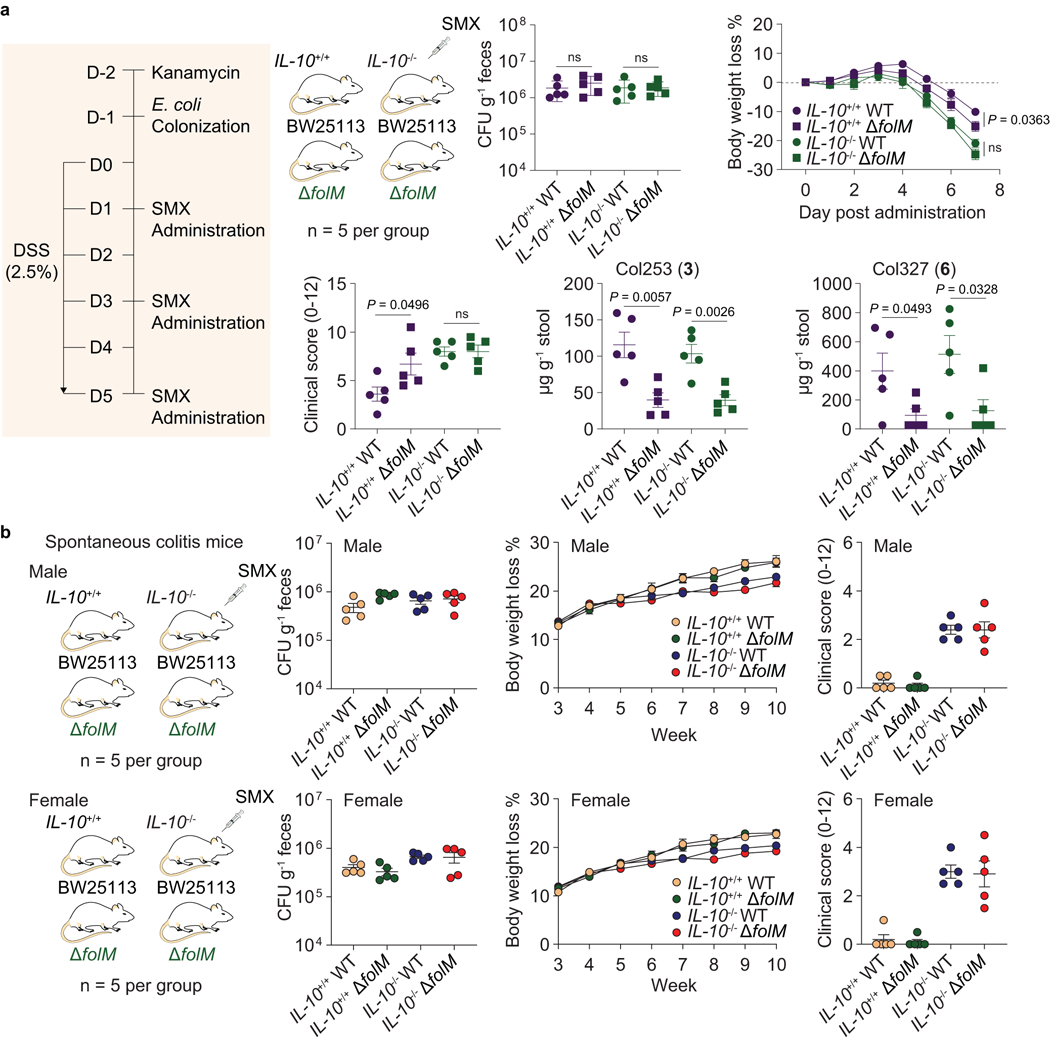
a, Primary evaluation on the reduction of colitis severity in SMX-treated colitis mice (IL-10+/+ and IL-10−/−) that were colonized with E. coli (wild-type E. coli BW25113. and its folM mutant strain). CFUs, body weight, and clinical scores were obtained as the same procedure that we described in Fig 4. HR-ESI-QTOF-MS quantification of colipterins 3 and 6 in stool samples. P values were determined by a two-tailed unpaired t-test. Error bars represent mean ± s.e.m.; ns, not significant. b, Effects of SMX-treated E. coli (wild-type E. coli BW25113 and its folM mutant strain) in the IL-10−/− male and female mice that spontaneously develop colitis. IL-10+/+ male and female mice that no spontaneous colitis develop were used as control groups. E. coli was colonized at week-3. CFUs were measured at 3 weeks after colonization. Body weight was monitored weekly. SMX was mixed in the drinking water at 0.3 mg ml−1 after the E. coli colonization. At week-10, endoscopy was performed and clinical scores were used as a metric of colitis severity. Data are presented by mean ± s.e.m. (error bars)
