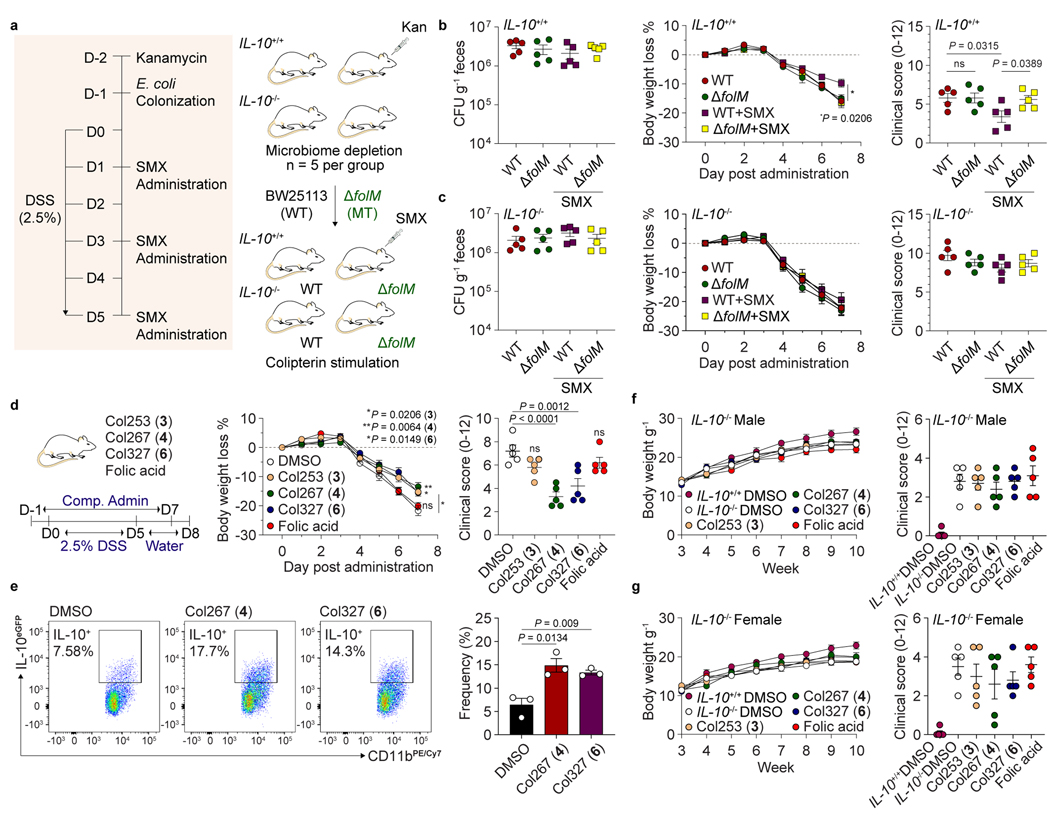
Fig. 4. Colipterins reduce colitis severity in an IL-10-dependent manner.
a, Experimental workflow for the intestinal colonization of E. coli (wild-type E. coli BW25113 and its folM mutant strain) followed by 2.5% DSS and SMX (100 mg kg−1 of body weight) administrations to mice (IL-10+/+ and IL-10−/−). b and c, Ameliorative effect of the severe colitis symptom in the DSS-induced IL-10+/+ (b) and IL-10−/− (c) colitis mice that were colonized with BW25113 or with a folM mutant, and these groups were treated with or without SMX. Colony-Forming Units (CFUs) in fecal pellets were measured at day 7 after DSS-administration. Body weight of each mouse was determined daily after DSS-administration, and the body weight loss was depicted as the percentage (%) compared to the initial body weight. Endoscopy clinical scores of each experimental group at day 6 after DSS administration. P value between WT (red) and WT+SMX (purple) is presented for body weight loss % in panel b. d, Reduction of severe colitis symptom by the administration of colipterins 3, 4, and 6. Folic acid was used as a control. Colipterins 3, 4, 6 and folic acid (each 10 mg kg−1) every other day to WT mice in DSS models. P values of DMSO versus treated compounds are presented. e, Representative and statistical percentage of IL-10eGFP positive cells among colon intestinal macrophages after administration of 4 and 6. Three biologically independent mice were used (n = 3). FACS sequential gating strategy is shown in Supplementary Figure 66. f and g, Evaluation of colipterins in the IL-10−/− male (f) and female (g) mice that spontaneously develop colitis. IL-10+/+ mice administered with DMSO were used as control. Body weight was monitored weekly. Compounds were mixed in the drinking water at 0.03 mg ml−1 individually after the mice were 6 weeks old. At week-10, endoscopy was performed and clinical scores were used as a metric of colitis severity. All P values were calculated by a two-tailed unpaired t-test. All error bars are represented as mean values ± s.e.m.; ns, not significant.