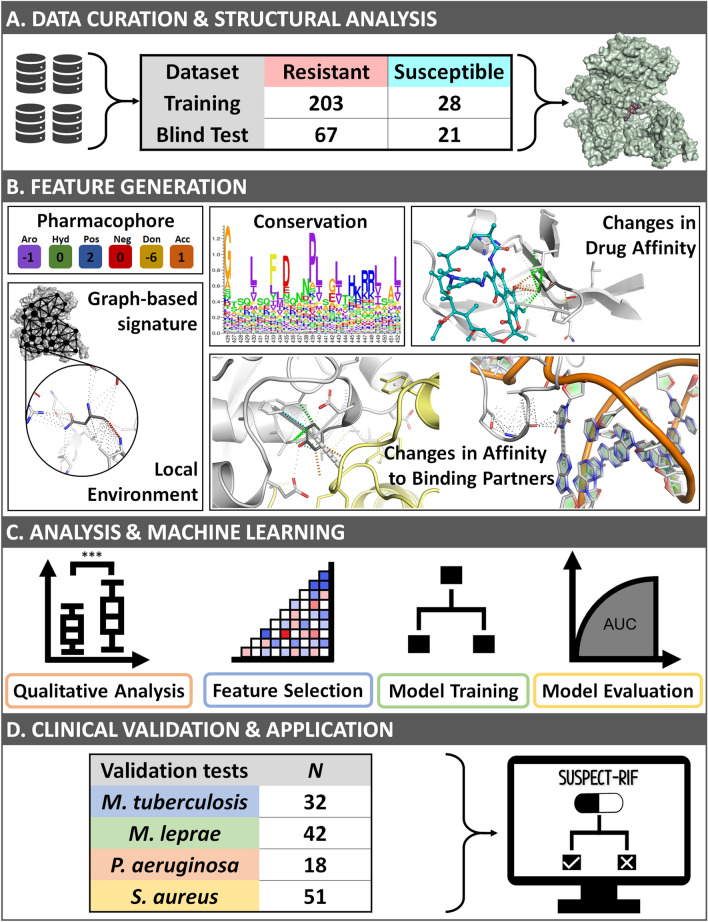
Figure 1.
Overview of SUSPECT-RIF workflow. Mutational data was manually curated from the literature, followed by structural analysis to ensure high data quality (A). Structural and Sequence-based properties were calculated and their ability to distinguish between mutation classes was assessed (B). Evolutionary and biological insights were used to train a machine learning classifier to accurately identify novel resistant and susceptible variants (C). Evaluation of the final model across blind clinical test sets from M. tuberculosis showed high performance and accurately identified clinical resistance variants from M. leprae, P. aeruginosa and S. aureus (D). SUSPECT-RIF is
available at https://biosig.unimelb.edu.au/suspect_rif.