Figure 2.
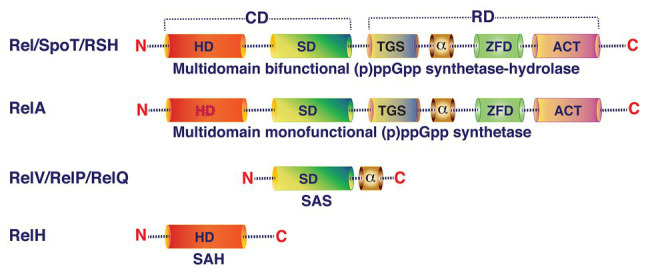
Schematic representation of the domain organization of (p)ppGpp synthetase/hydrolase family of proteins. Bifunctional long multidomain (p)ppGpp synthetase-hydrolase and monofunctional long multidomain (p)ppGpp synthetase enzymes are composed of two regions: (i) N-terminal catalytic domain (CD) and (ii) C-terminal regulatory domain (RD). Both synthetase and hydrolase domains (SD and HD, respectively) are functional in bifunctional enzymes (Rel/RSH/SpoT). In monofunctional multidomain, (p)ppGpp synthetase enzyme (RelA) hydrolase activity is lost due to accumulation of spontaneous mutations in the catalytic residues. The C-terminal regulatory region of the multidomain protein contains TGS domain (ThrRS, GTPase, and SpoT), conserved α helical domain, ZFD domain (zinc-finger or conserved cysteine domain), and ACT (aspartate kinase, chorismate, and TyrA) RNA recognition motif. The small alarmone synthetase (SAS) enzyme (RelV/RelP/RelQ) contains SD and a small oligomeric α-domain. The RelH/small alarmone hydrolase (SAH) contains only the HD.
