Figure 3.
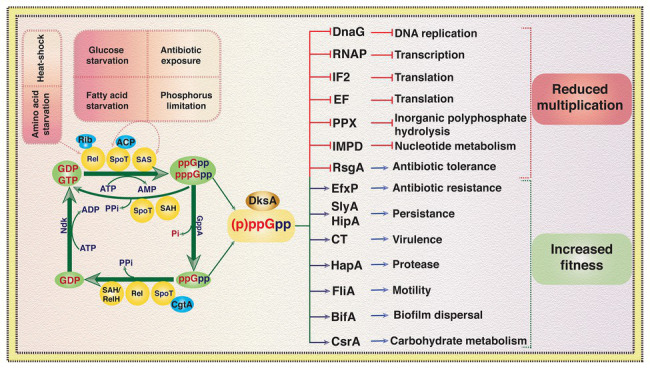
An overview of signaling, metabolism, and effect of (p)ppGpp in virulence, antibiotic resistance, and other cellular processes in bacteria. GDP and GTP are converted to (p)ppGpp during stress conditions or upon exposure to xenobiotics due to transfer of a pyrophosphate moiety from ATP to the 3'-OH position of ribosugar of guanosine nucleotide. GTP pyrophospho kinase activity of Rel, SpoT, and SAS can mediate the transfer of pyrophosphate to GTP or GDP depending on the stress signaling and activity of other cellular proteins like acyl carrier protein (ACP) and functional state of protein synthesis machinery, i.e., ribosome (Rib). pppGpp can be converted to ppGpp due to phosphatase activity of GppA. SpoT, Rel, and SAH can hydrolyze the pyrophosphate moiety from 3'-OH position of pppGpp and ppGpp and generate GTP or GDP, respectively. Guanine nucleotide binding protein of the Obg/GTP1 subfamily CgtA induces (p)ppGpp hydrolase activity of SpoT. Nucleoside diphosphate kinase (Ndk) converts GDP to GTP using ATP as phosphate donor. Elevated intracellular level of (p)ppGpp independently or in conjunction with transcriptional factor DksA regulates several cellular processes including DNA replication, transcription, protein biosynthesis, carbohydrate metabolism, virulence, motility, antibiotic resistance, and biofilms formation. (p)ppGpp regulates several proteins involved in nucleotide metabolism, persistence, antibiotic resistance, etc., however, for simplicity, a representative protein for each case is depicted here and more details can be found in the references cited. SAS, small alarmone synthase; SAH, small alarmone hydrolase; GppA, guanosine-5'-triphosphate, 3'-diphosphate pyrophosphatase; DnaG, DNA primase; RNAP, RNA polymerase; IF2, initiation factor 2; EF, elongation factor; PPX, exopolyphosphatase; IMPD, inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase; RsgA, small ribosomal subunit biogenesis GTPase; EfxP, efflux pumps; SlyA, transcriptional regulator of Salmonella enterica; HipA, toxin component of Escherichia coli TA module; CT, cholera toxin; HapA, hemagglutinin protease; FliA, flagella regulatory sigma factor; BifA, biofilm formation protein; CsrA, carbon storage regulator (Dalebroux et al., 2010; Ronneau and Hallez, 2019; and the references therein).
