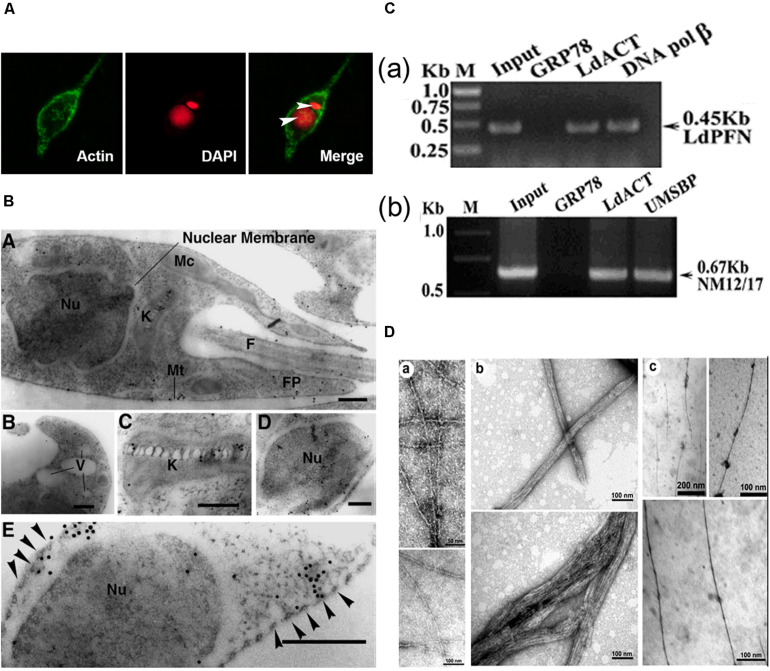
FIGURE 4.
(A) Immunofluorescence micrograph of Leishmania promastigotes after treating them with 0. 5% NP-40 and staining with anti-LdAct antibodies and DAPI showing the presence of LdAct in the nucleus and kinetoplast and its association with nuclear DNA and kDNA (adapted from Sahasrabuddhe et al., 2004 with permission). (B) Electron micrographs of immunogold-labeled actin showing the presence (panel a) of LdAct in the nucleus (Nu), the kinetoplast (K), the flagellum (F), and the flagellar pocket (FP). In addition, the presence of LdAct on membranes of vacuoles (V) may also be noticed in panel (b), and its associations with kDNA network, nuclear membrane and subpellicular microtubules may clearly be seen in panels (c–e), respectively. The arrowheads in panel (e) mark the microtubules. Bar, 200 nm (Adapted from Sahasrabuddhe et al., 2004 with permission). (C) Chromatin Immuno-precipitation (ChIP) analysis using anti-LdAct antibodies showing the in vivo association of LdAct with chromatin (a) and kDNA network (b). Panels (a,b) are the agarose gels of PCR products after ChIP assay. Lanes are marked on the top with their respective antibodies used in the ChIP assay and arrows indicated the genes amplified after pull down. An irrelevant, non-DNA associating antibody, GRP78, was used as a negative control, whereas antibodies against DNA polβ, and UMSBP (universal minicircle sequence-binding protein), were used as positive controls for nuclear DNA and kDNA respectively. LdPfn, Leishmania profilin; NM12/17, specific minicircle primers (this was originally published in Nucleic Acids Research, Kapoor et al., 2010© Oxford University Press). (D,a) Negatively stained transmission electron micrograph of in vitro reconstituted rabbit muscle actin (RbAct) filaments in F-buffer (100 mM KCl, 2 mM MgCl2 and 2 mMATP; pH 8.0; 25°C) and (b) LdAct at 2 μM protein concentration, unlike RbAct, formed bundles rather thin filaments, under identical conditions. (c) LdAct forms very thin filaments at 0.2 μM G-LdAct concentration in F-buffer, pH7.0 at 25°C. RbAct under these conditions failed to form filaments (taken from Kapoor et al., 2008 with permission).