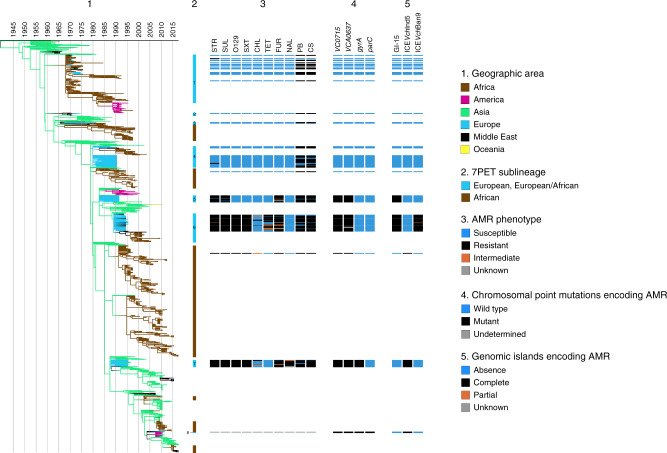
Fig. 3. Phenotypic and genetic characterization of antibiotic resistance in the European seventh pandemic V. cholerae O1 El Tor isolates analyzed here.
(1) Timed phylogeny, identical to that in Fig. 1, but represented vertically. (2) The seventh pandemic V. cholerae O1 El Tor (7PET) sublineages are indicated. The names of the European and European/African sublineages are indicated by a one-digit number within or next to the blue line and corresponding to that found in the sublineage name (e.g., 1 for EUR1, 2 for EUR2/AFR3, etc). The antimicrobial resistance (AMR) phenotype for 10 antibiotics, the presence of chromosomal AMR genes (4), and genomic islands encoding AMR (5) are shown for each isolate, according to its position in the phylogeny. More detail about the genes and genomic islands encoding AMR is provided in the footnotes of Table 3. The abbreviations used for the antibiotics are as follows: STR streptomycin; SUL sulfonamides; O129 vibriostatic agent O/129; SXT trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole; CHL chloramphenicol; TET tetracycline; FUR furazolidone; NAL nalidixic acid; PB polymyxin B; CS colistin. Note that 18 European isolates identified as outliers (Supplementary Data 1) are not represented in this timed phylogeny.