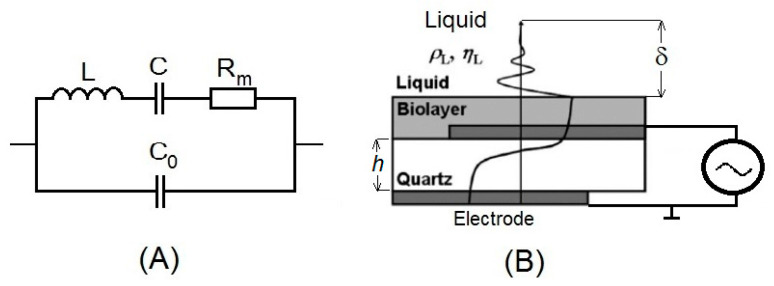
Figure 3.
(A) Butterworth-van-Dyke (BvD) equivalent circuit. C0 = εA/h is the parallel electrical capacitance, L = 1/ω2C is the motional inductance (proportional to the mass), C = 8K2C0/(Nπ)2 is the motional capacitance (inversely proportional to the stiffness) and Rm = ηq/μqC is the motional resistance related to the dissipative losses. A is the electrode area, ε and h are the dielectric permittivity and thickness of the crystal, respectively, ω = 2πf, where f is series resonant frequency, K is the electromechanical coupling coefficient and N is the integer. ηq is the effective viscosity, and μq is the shear stiffness. (B) Scheme of the propagation of the acoustic wave. ηL and ρL are the viscosity and density of the liquid, respectively. δ is the penetration depth.