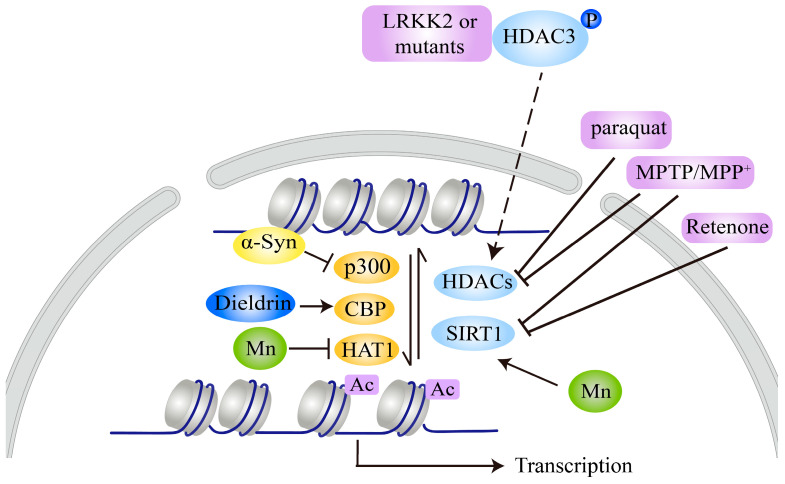
Figure 2.
Lysine acetylation of histones mediated by PD-related neurotoxins and genetic factors. MPTP/MPP+, rotenone, paraquat, or dieldrin treatment leads to hyperacetylation of H3 and/or H4 by decreasing the activity or expression of certain HDACs or SIRT1 or by increasing CBP expression. α-syn causes hypoacetylation of H3 by binding to histones or inhibiting p300 expression and activity. LRKK2 or its mutants repress H4 acetylation by phosphorylating HDAC3 and promoting its nuclear translocation to increase its activity. Mn decreases H3 and H4 acetylation by increasing HDAC3/4 expression and decreasing HAT1 expression, respectively.