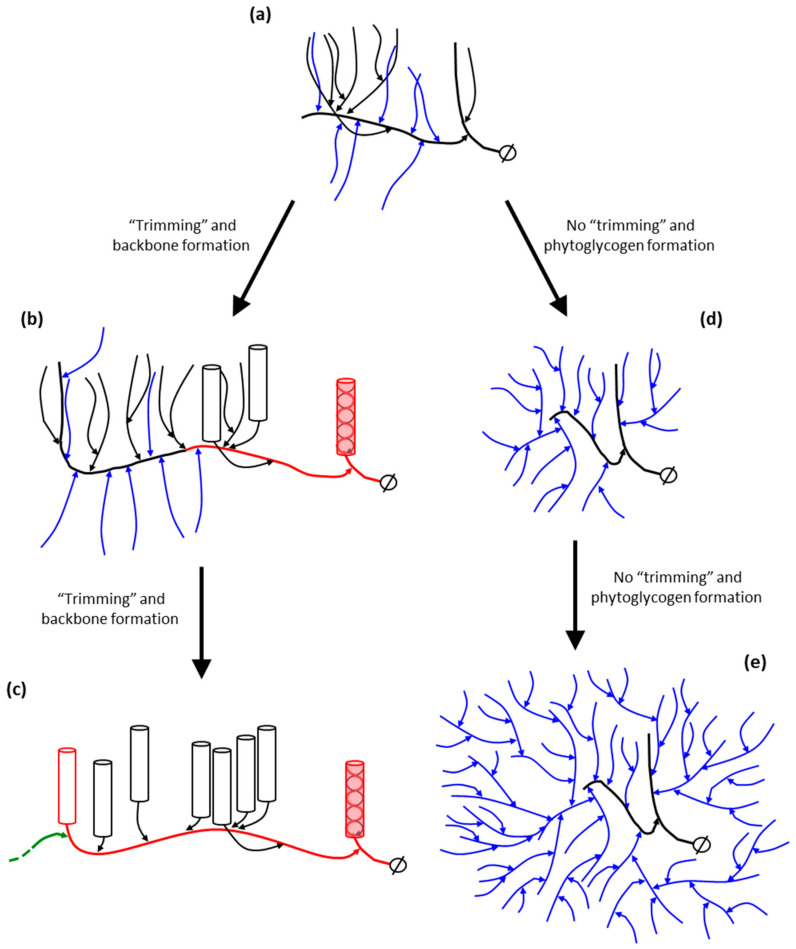
Figure 6.
The trimming hypothesis of amylopectin adapted to the backbone model. (a) A “pre-amylopectin” is formed by the action of SSs and SBE, having a tightly branched structure. (b) The “pre-amylopectin” is “trimmed” through removal of chains (blue) by the action of DBE to form the backbone (red) with characteristic inter-block segments between the branched building blocks. The short chains that remain after the trimming form double-helices (cylinders). External chains of the long chains forming the backbone participate in double-helices (red cylinders). The backbone chain is elongated and extensively branched simultaneously with the trimming events. (c) The elongated structure is trimmed and the backbone continuous to be elongated eventually, with a new chain stub (green) introduced by SBEs. (d) An extensively branched molecule is formed without the trimming action, and (e) a water-souble phytoglycogen molecule is eventually the result of a continuous branching and chain elongation in the absence of DBE activity.