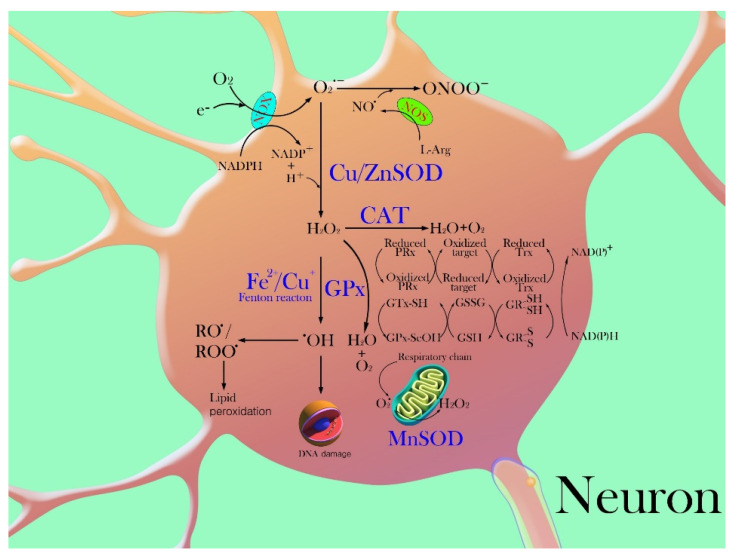
Figure 2.
Enzymatic antioxidant defense system against the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Various pathways of cell death caused by ROS and its transformation are observed in brain injury. NADPH oxidase and mitochondrial respiratory transport chain are known as major cellular sources of the superoxide radical anion (O2−). The superoxide radical anion reacts with nitric oxide (NO) to form the peroxynitrite anion (ONOO−) which mediates oxidative modification of protein residues via an interaction with NO. The superoxide radical is dismuted by the superoxide dismutase enzyme (SOD) to form hydrogen peroxide. In addition, manganese containing superoxide dismutase (Mn-SOD) reduces the superoxide radical anion generated during the electron transport chain in the mitochondrial matrix. Catalase (CAT) and/or glutathione peroxidase (GPx) decomposes hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen by enzymatic reactions. Hydrogen peroxide is decomposed into reactive hydroxyl radicals by reaction with catalytically active redox metals such as (copper and iron). Hydroxyl radicals can react with oxygen to form peroxyl or alkoxyl radicals which can lead to lipid peroxidation and react with DNA and primarily cause damage to DNA. Peroxiredoxins (Prx) and thioredoxin (Trx) act as redox-regulated proteins to additional redox relay bases.