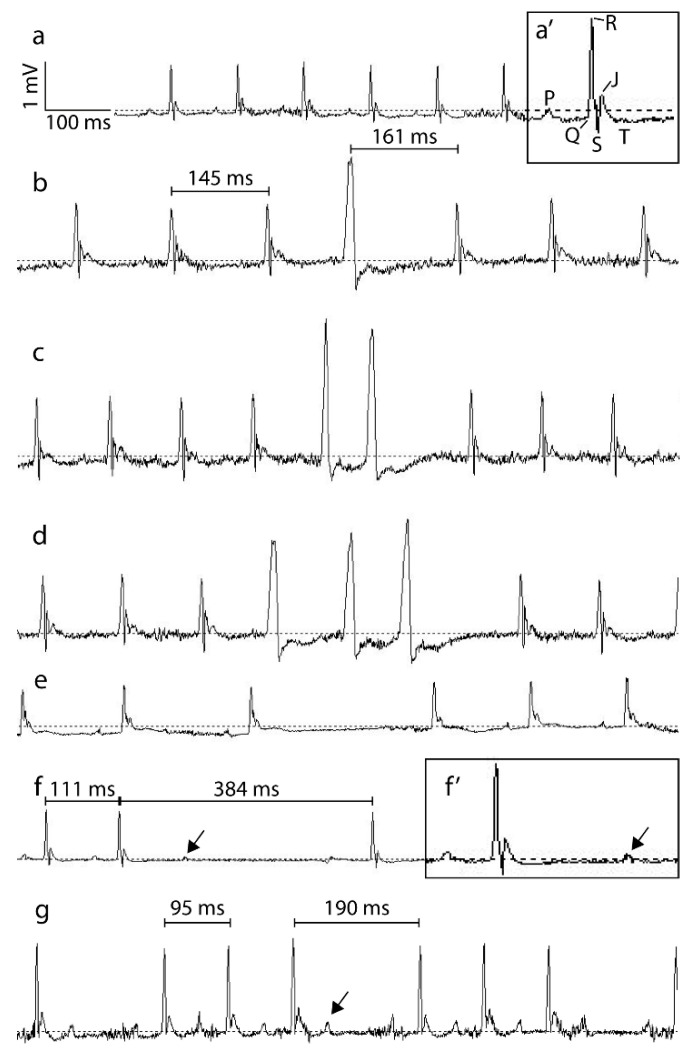
Figure A2.
Representative traces of arrhythmic events. (a): murine ECG trace in sinus rhythm. (a’): two-fold magnification of the murine ECG trace of a single heart beat in sinus rhythm marked with the different components: the P-wave (P), the QRS-complex (QRS), the J-wave (J), and the T-wave (T). (b): murine ECG trace with extrasystole, single. An extrasystole is described as an extra heart beat either originating from supraventricular, ventricular or near junctional cardiac tissue. This is represented as an extra QRS-complex with an abnormal morphology, mostly followed by a deviant compensatory longer RR-interval (indicated with brackets). (c): murine ECG trace with extrasystole, doublet. A doublet is represented as two consecutive extrasystoles. (d): murine ECG trace with three consecutive extrasystoles. (e): murine ECG trace with sinus arrest. A sinus arrest is represented by a long RR-interval within the ECG trace in the absence of any ECG activity. (f): murine ECG trace with blocked P-wave. A blocked P-wave is represented by the presence of a P-wave (indicated with arrow) without subsequent QRS-complex. The resulting long RR-interval is not a multiple of the normal mean RR-interval. (f’): two-fold magnification of a murine ECG-trace with blocked P-wave. Presence of P-wave is indicated with arrow. (g): murine ECG trace with AV-Block. An AV-block is represented by the presence of a P-wave (indicated with arrow) without subsequent QRS-complex. The resulting long RR-interval is a multiple of the normal mean RR-interval. The vertical and horizontal scale bar represent 1 mV and 100 ms, respectively.