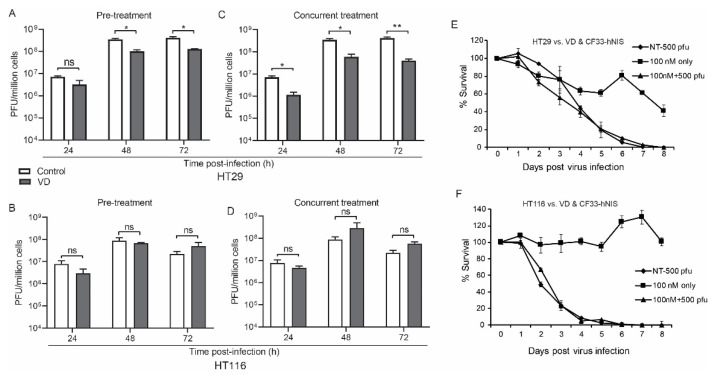
Figure 1.
Vitamin D (VD) analogue does not directly affect viral replication. Human colon cancer cells HT29 (A) and HCT116 (B) were pre-treated with VD or phosphate buffered saline (PBS) for 12 and 14 days respectively and then infected with CF33-hNIS at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 0.01 and analyzed daily for 3 days via standard viral plaque assay. Abrogated viral replication in VD-responsive HT29 cells (C) versus non-responsive HCT116 cells (D) is still more pronounced when cells were concurrently treated and that treatment was continued after viral infection. Cytotoxicity assays over extended period of time with 6 days of VD pre-treatment followed by virus infection alone at a standardized dose rather than MOI are shown for HT29 (E) and HCT116 (F) cells. Stat = non-paired t-test, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, error bars = standard deviation, ns = non-significant.