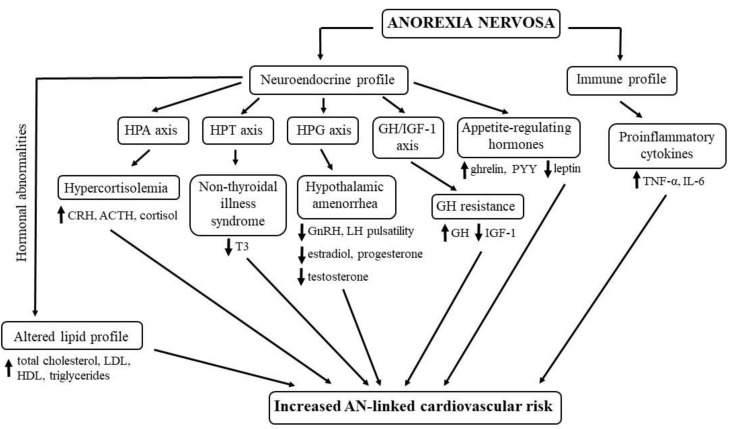
Figure 1.
The complex neuroendocrine–immune pathways leading to a higher risk of cardiovascular diseases in anorexia nervosa. HPA, hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal; HPT, hypothalamic–pituitary–thyroid; HPG, hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal; GH, growth hormone; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor 1; CRH, corticotropin-releasing hormone; ACTH, adrenocorticotropic hormone; T3, triiodothyronine; GnRH, gonadotropin-releasing hormone; LH, luteinizing hormone; PYY, peptide YY; TNF-α, tumour necrosis factor α; IL-6, interleukin 6; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; HDL, high-density lipoprotein; AN, anorexia nervosa; up-arrow, increased levels; down-arrow, decreased levels.