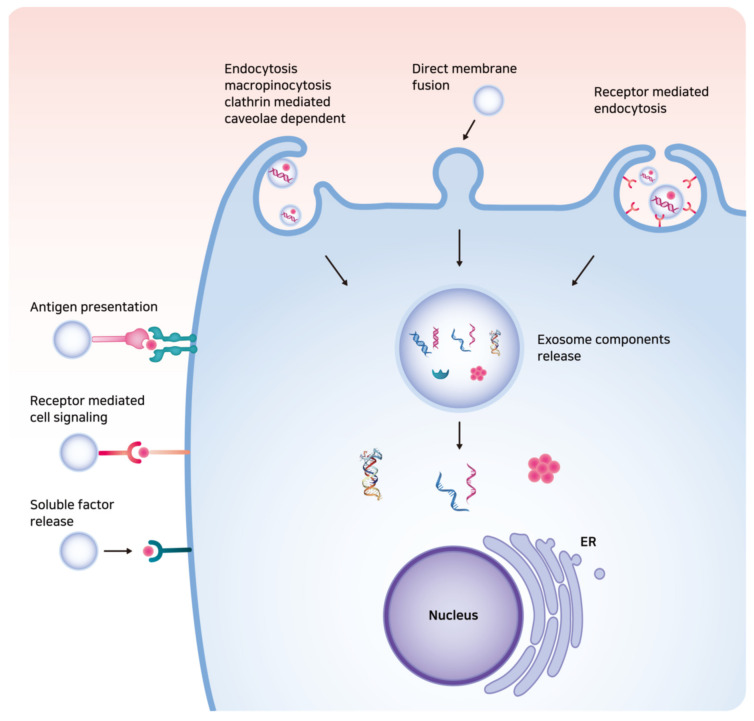
Figure 2.
The illustration of exosome–cell interaction. Exosomes can be taken up into the recipient cell via direct membrane fusion or endocytosis, leading to the delivery of exosomal contents such as DNAs, messenger RNAs, long non-coding RNAs, enzymes, and signaling peptides or proteins to the cytosolic space of the recipient cell. Receptor-ligand interactions between cell surface receptors and exosomal ligands may also occur.