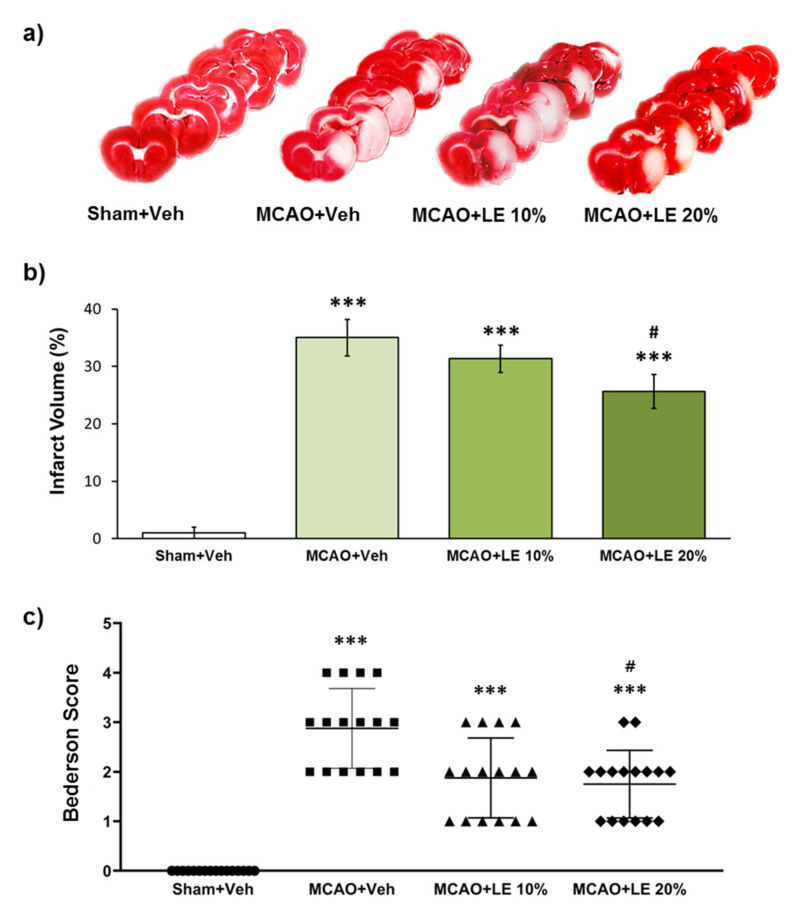
Figure 1.
Neuroprotective effects of lipid emulsion (LE) or vehicle (Veh) after the middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) and reperfusion injury. (a) Triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC)-stained brain slices for infarction measurement. Decrease in infarction volumes were observed in MCAO+LE 10% and MCAO+LE 20% groups. Sham group did not show ischemic reperfusion injury; (b) Measurement of infarction volume from TTC staining. The MCAO+Veh group increased significantly in infarction volume compared to Sham+Veh group. Both MCAO+LE 10% and MCAO+LE 20% decreased in infarction volume but only the MCAO+LE 20% group had significant difference compared to the MCAO+Veh group; (c) Bederson scores of the experimental groups. The MCAO+Veh group increased in Bederson score significantly compared to Sham+Veh group. Both MCAO+LE 10% and MCAO+LE 20% groups decreased in Bederson scores compared to MCAO+Veh group; however, only the MCAO+LE 20% group decreased significantly. Data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM); n = 16 for each group; *** p < 0.001 vs. Sham+Veh, # p < 0.05 vs. MCAO+Veh. Statistical analysis for the measurement of infarction volume was performed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test. Statistical analysis for Bederson scores was performed using Kruskal-Wallis non-parametric test followed by Dunn’s post hoc test.