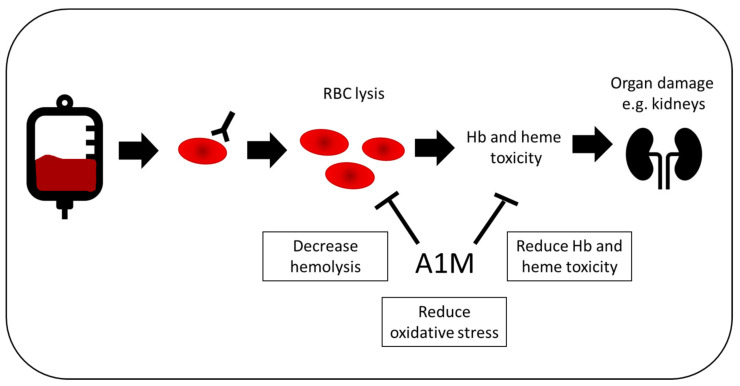
Figure 5.
Potential therapeutic effect in blood transfusion. In patients receiving blood, 1–2% will produce antibodies to a blood group, increasing the risk of acute or delayed hemolysis. This is linked to organ damage, such as renal damage, which can be both transient and permanent. A1M could be used as a treatment during blood transfusions, in order to decrease both hemolysis and the resulting oxidative damage of free Hb and heme.