Figure 7.
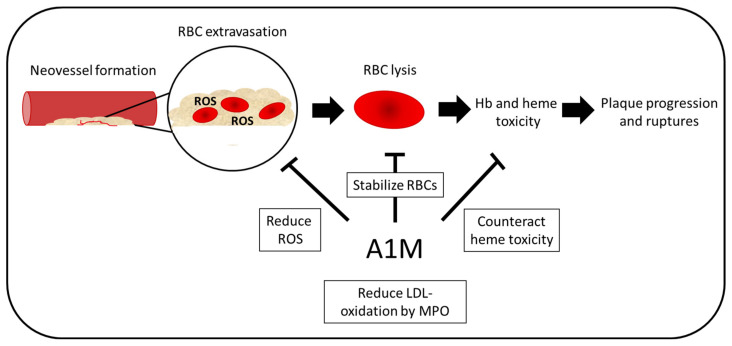
Potential therapeutic effect in atherosclerosis. In atherosclerosis, neovascularization is increased in unstable plaques. These vessels are often leaky, which leads to RBC extravasation within the plaques. Due to high presence of ROS, the RBCs lyse, which leads to increased oxidative stress and, therefore, further plaque progression and ruptures. A1M could have multiple protective functions including battling heme toxicity and ROS as well as stabilizing the RBCs. Moreover, LDL oxidation by MPO, a feature known to contribute to the progression of atherosclerosis, which is inhibited by A1M.