Figure 4.
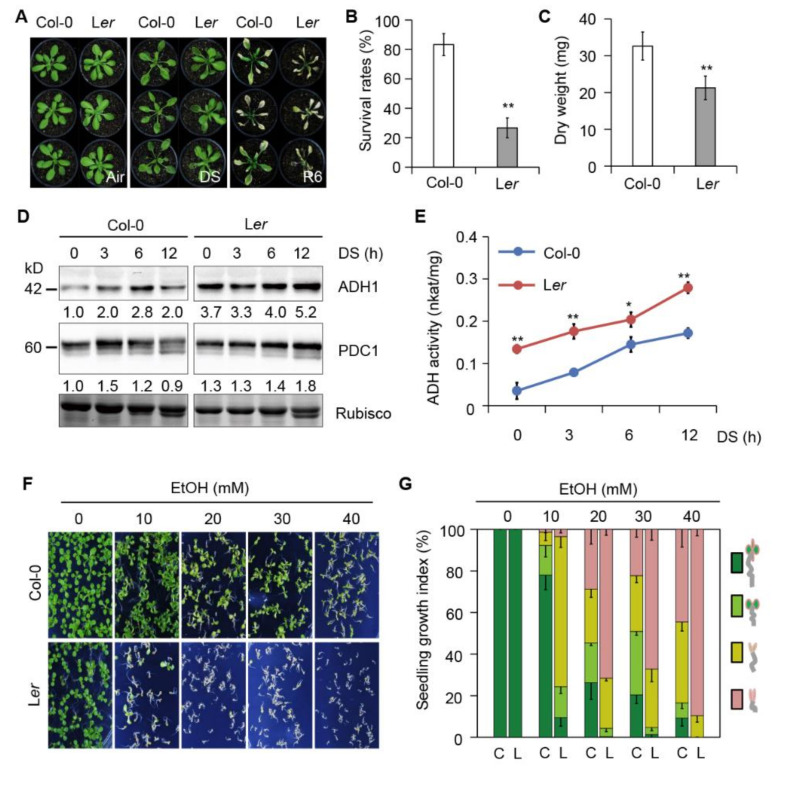
Two Arabidopsis accessions with different levels of submergence tolerance show different responses to ethanol. (A) Phenotypes of 4-week-old Columbia (Col-0) and Landsberg erecta (Ler) plants before submergence (Air) and after 60 h of dark submergence (DS), followed by recovery for 6 d (R6). The experiments were repeated three times with similar results. (B) and (C) survival rate (B) and dry weights (C) of Col-0 and Ler plants after DS treatment followed by recovery for 6 d. Data are means (± SD) of three biological replicates. For each biological repetition, 15 plants were used per accession. Asterisks indicate significant differences between Col-0 and Ler, as determined by Student’s t-test (** P < 0.01). (D) Protein abundance of ADH1 and PDC1 in 4-week-old Col-0 and Ler plants treated with dark submergence (DS) at various time points. Numbers below the protein bands indicate relative gray values of the bands. Coomassie blue-stained Rubisco is shown as a loading control. The experiments were repeated three times with similar results. (E) Measurement of alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) activity in 2-week-old Col-0 and Ler plants after dark submergence (DS) treatment for 0, 3, 6, and 12 h. The experiments were biologically repeated three times with similar results. Error bars represent SD (n = 3 technical replicates). Asterisks indicate significant difference between Col-0 and Ler, as determined by Student’s t-test (* p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01). (F) Col-0 and Ler seedlings grown on MS medium supplemented with different concentrations of ethanol. Images were taken 10 d after germination. The experiments were repeated three times with similar results. (G) Seedling growth index in (F). The colors in the columns correspond to seedlings with true leaves (dark green), seedlings with green (light green) or brown (yellow) cotyledons, and etiolated seedlings (pink). Data are means (± SD) of three biological replicates. C, Col-0; L, Ler.