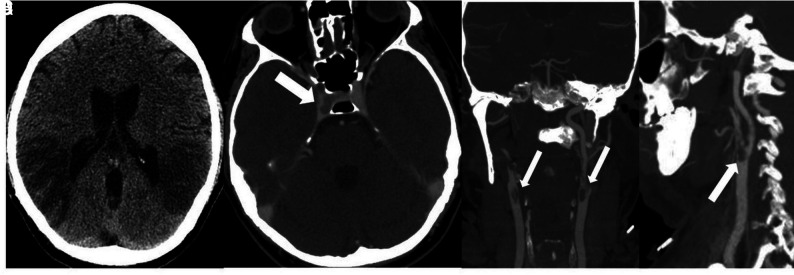
FIG 5.
Noncontrast CT (A) demonstrates low attenuation in the parietal and temporal lobes compatible with acute infarctions. Head CTV (B) demonstrates occlusion of the cavernous segment of the right internal carotid artery (arrow). Neck CTA (C and D) shows extensive intraluminal thrombi (arrows) in the distal common carotid arteries, extending to the carotid bulbs and external carotid arteries.