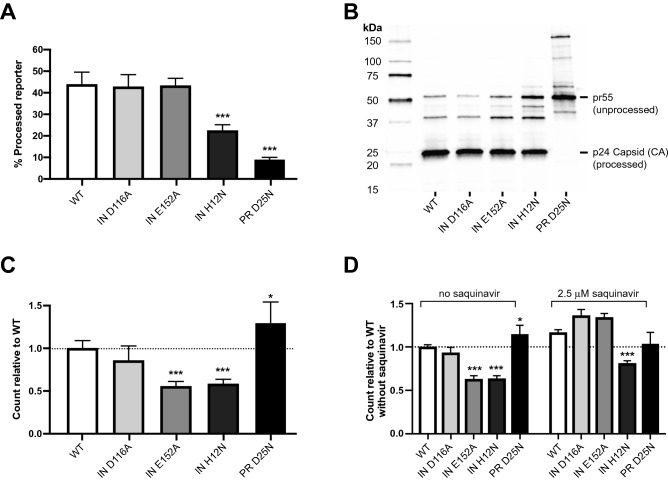
Figure 4.
NFC enables rapid detection of mutations affecting PR processing efficiency and virus release. (A) PR processing of VIPER with wild-type NL4-3, IN D116A, IN E152A, IN H12N, and PR D25N mutants, analyzed using NFC. The IN H12N and PR D25N mutations both significantly reduced processing efficiency (p < 0.0001 for both). (B) Western blot analysis of p24 CA processing with wild-type NL4-3 and mutant viruses. The PR D25N mutant resulted in severe disruption of Gag and Gag-Pol processing as expected for the catalytic site mutation. The IN H12N and E152A mutants resulted in slight elevations in unprocessed Gag and processing intermediates. (C) Release of HIV-1 viruses as measured by NFC. The IN E152A and H12N mutations resulted in significant reductions in virus release (p < 0.0001 for both). The PR D25N mutation resulted in a modest but significant increase in virus release (p = 0.021). (D) Virus release for the E152A mutant was fully restored by treating cells with saquinavir. However, the H12N mutant continued to demonstrate significantly reduced processing (p < 0.001) in the presence of saquinavir. Virus release in the absence of saquinavir is replotted from the data shown in part (C).