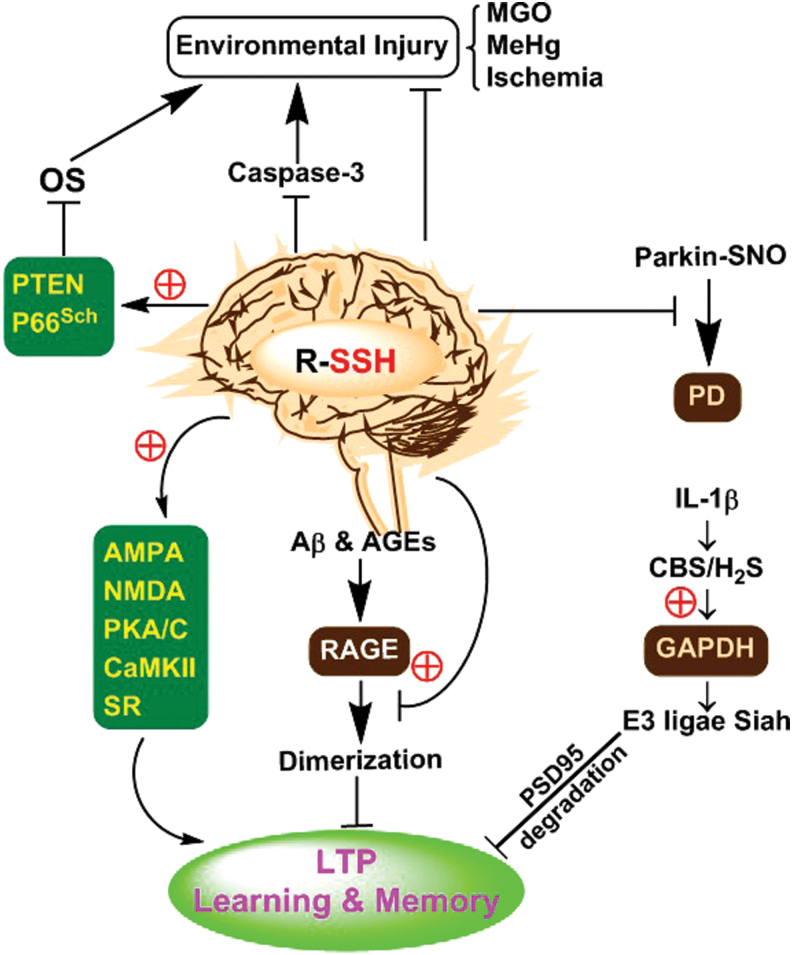
FIG. 3.
Possible signaling roles of S-persulfidation in the nervous system. S-Persulfidation of glutamate AMPA and NMDA receptors, postsynaptic proteins (PKA/C, CaMKII) and serine racemase is involved in normal learning and memory. S-Persulfidation of RAGE blunts Aβ and AGEs-impaired learning and memory. Proinflammatory cytokine IL-1β-mediated S-persulfidation of GAPDH harms learning and memory through degradation of PSD95. S-Persulfidation of parkin blocks its S-nitrosylation and inactivation and thus eliminates PD lesions. S-Persulfidation increases PTEN and P66Sch activity and decreases caspase-3 activity, thereby reducing environmental stimuli-induced neuronal lesions. Aβ, Abeta 1–42 peptide; AGE, advanced glycation end product; AMPA, α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid; CaMKII, calmodulin-dependent protein kinases II; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; IL, interleukin; NMDA, N-methyl-d-aspartate; PD, Parkinson's disease; PKA, protein kinase A; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; RAGE, receptor for advanced glycation end product. Color images are available online.