Figure 1.
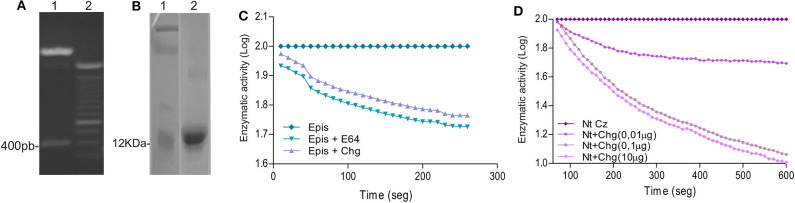
Cloning and characterization of Chg. (A) Digestion of pET23a+-Chg construction with the NdeI and HindIII restriction enzymes released the 400-bp Chg insert. (B) SDS-PAGE analysis of rChg expression in E. coli BL21 and purification under native condition. Lane 1: MW marker; Lane 2: IMAC Ni-NTA purified rChg (12 kDa) stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue. (C) Relative enzymatic activity of T. cruzi epimastigote lysate (5 μM) in the presence of rChg (10 μM) or synthetic inhibitor E-64 (10 μM) on the fluorogenic substrate Z-Gly-Pro-AMC (6 μg) measured as relative fluorescent units (RFUs) and expressed as the log of the percentage of the fluorescence units as a function of time. (D) Cysteine protease activity of the rNtCz in the absence or presence of increasing concentrations of rChg (0.01–10 μg).