Figure 3.
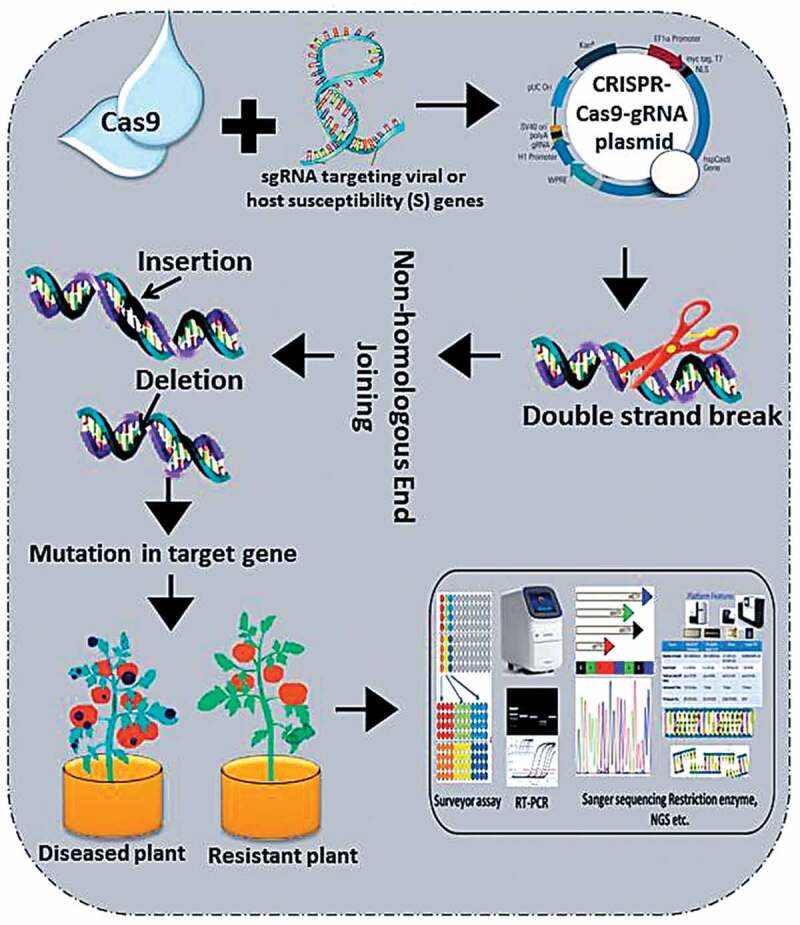
General work-flow of developing disease ressistance crops using CRISPR-Cas9 system
Plant genome editing typically follow these steps: Finding a target gene and construction of artifical sgRNA, Vector construction follwoed by plant transformation. After transformation, sgRNA directs the Cas9 protein to bind target sequence and induce DSB. This DSB causes random mutations is repaired by error-prone HDR pathway based on the experimental objective. Plants with altered genome (with induced or deleted genes) is further screened and analysezed for desired trait. CRISPR, clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat; Cas, CRISPR-associated; DSB, double-strand break; HDR, homology-directed repair; NHEJ, non-homologous end-joining; sgRNA, singleguide RNA.
