Extended Data Fig.3|. uPAR is a marker of senescence in senescence-associated human pathologies.
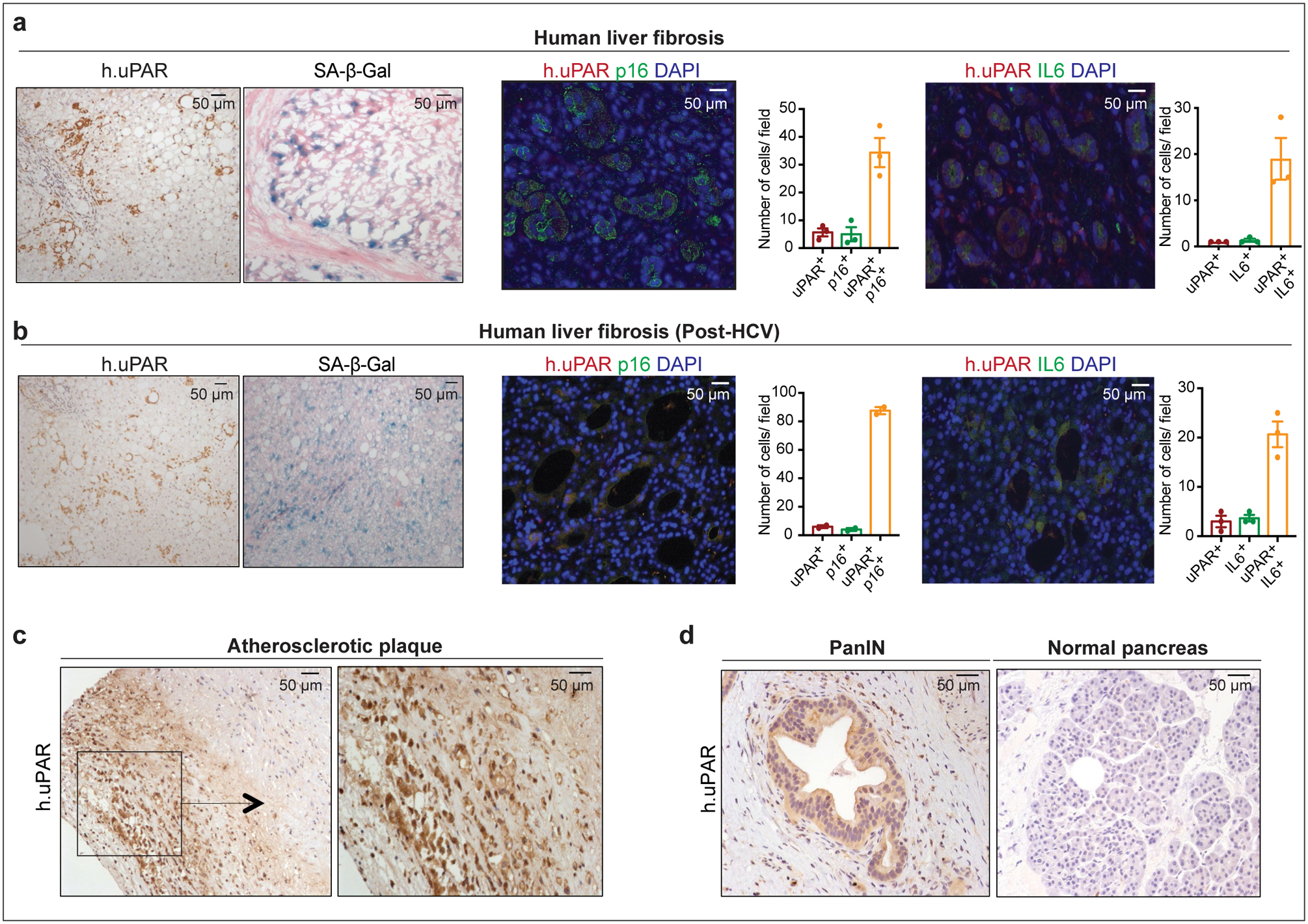
(a) Immunohistochemical expression of human uPAR (h.uPAR) and SA-β-Gal in human samples of hepatitis-induced liver fibrosis (n=7 patients). Co-immunofluorescence staining and quantification of human uPAR (red) and p16 (green) or human uPAR (red) and IL6 (green) in human samples of hepatitis-induced liver fibrosis (n=3). (b) Immunohistchemical expression of human uPAR (h.uPAR) and SA-β-Gal in human samples from patients with eradicated hepatitis C virus (HCV) and residual liver fibrosis (n=7 patients). Co-immunofluorescence staining and quantification of human uPAR (red) and p16 (green) or human uPAR (red) and IL6 (green) in human samples of HCV-induced liver fibrosis (n=3). (c) Immunohistochemical stainings of human uPAR (h.uPAR) in human carotid endarterectomy samples (n= 5 patients). (d) Immunohistochemical stainings of human uPAR (h.uPAR) in human pancreas bearing pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PanINs) compared to normal pancreas controls (n= 3 patients). (a,b) Data represent mean± SEM.
