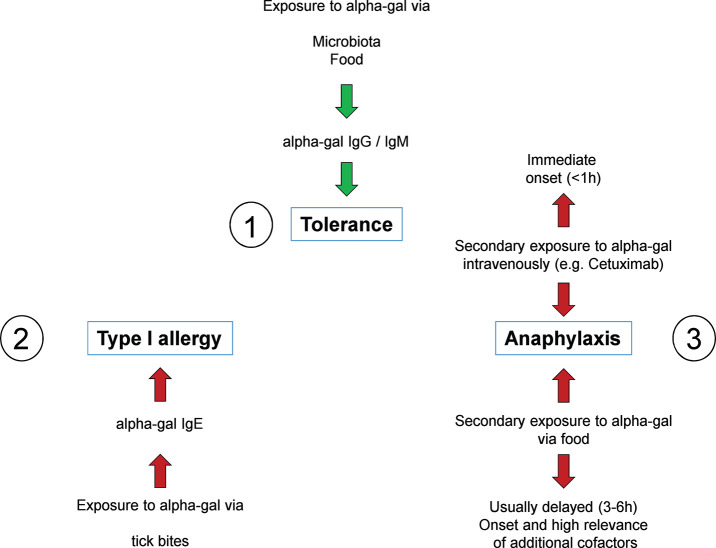
Figure 3.
The alpha-gal syndrome. All individuals initially develop tolerance to alpha-gal mediated by constant exposure through bacterial colonization of the intestine and potentially also to food, associated with alpha-gal specific IgG and IgM antibodies (1). However, in some individuals, repetitive tick bites can result in a break of tolerance by induction of alpha-gal specific IgE (2). Upon consumption of red meat and innards as well as administration of alpha-gal containing drugs such as the therapeutic monoclonal antibody cetuximab, these individuals experience symptoms up to fatal anaphylaxis. While symptoms in response to cetuximab occur immediately after administration, anaphylaxis in response to red meat or innards occurs in a delayed fashion 3–6 h after consumption (3).