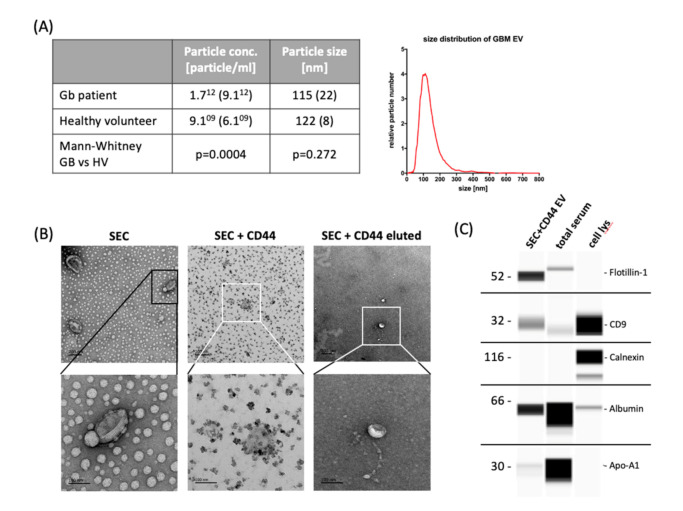
Figure 1.
Yield and characteristics of serum-derived extracellular vesicles. (A) NTA of extracellular vesicles (EVs) isolated from 500 µL serum by size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) to determine the yield and particle size. The table states the mean particle concentration and mean modal size of 55 glioblastoma patients and 5 healthy volunteers (HV). Standard deviation is given in parentheses; histograms: exemplary size distribution of glioblastoma-EVs measured by NTA. (B) Transmission electron microscopy images showing the typical EV morphology. Scale bar represents, in all images, 200 nm in the upper row (30k × magnification) and 100 nm in the lower row (110k × magnification). Images in the left lane show EVs after SEC, middle lane images show CD44-captured SEC-EVs, and right lane images represent EVs that were diluted from CD44-beads. (C) Wes ProteinSimple immunodetection confirming the presence of the EV-markers flotillin-1 and CD9 and the absence of non-EV protein calnexin in SEC + CD44 EV preparations. Cell and total serum lysates were used as positive controls for the non-EV marker calnexin, apolipoprotein A1, and serum albumin, respectively. NTA = nanoparticle tracking analysis; cell lys = cell lysate of PBMCs (1:10) or glioblastoma cell line Gli36 (1:100); Apo-A1 = apolipoprotein A1.