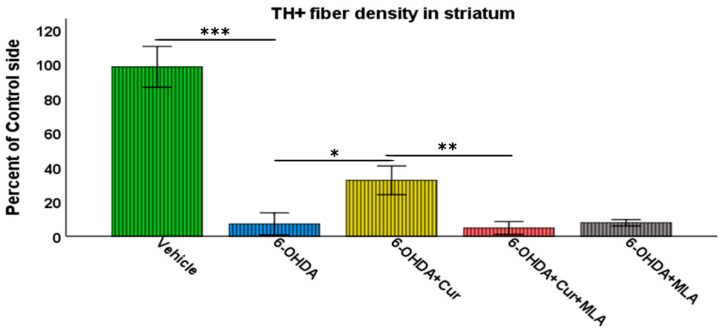
Figure 3.
Striatal TH-immunoreactive fiber density expressed as a percentage of the fiber density on the lesioned side to the non-lesioned side. The density was measured at four rostro-caudal levels of the striatum: rostral (+1.56 mm), middle 1 (+0.72 mm), middle 2 (+0.12 mm), and caudal (−0.24 mm) relative to the bregma. The multiple intra-striatal 6-OHDA injections caused extensive damage to TH-positive fibers throughout the four levels of striatum compared with the vehicle-treated group (ANOVA, p ˂ 0.000 ***). The neuroprotective effect of curcumin, through an α7-receptor-mediated mechanism, was marked in the curcumin-treated group at all rostro-caudal levels of striatum in comparison with the 6-OHDA-injected group (ANOVA, p ˂ 0.011 *). MLA, an α7-receptor blocker, reversed the protective effect of curcumin in the 6-OHDA+Cur+MLA group in comparison with the 6-OHDA+Cur-treated group (ANOVA, p ˂ 0.005 ** at all levels). The MLA antagonist had no effect by itself, as indicated by the last group of animals (6-OHDA+MLA) and exhibited no statistical difference from the 6-OHDA+Cur+MLA group or 6-OHDA injected rats at all levels (ANOVA, NS). Values represent mean % of control side ± 2 SEM.