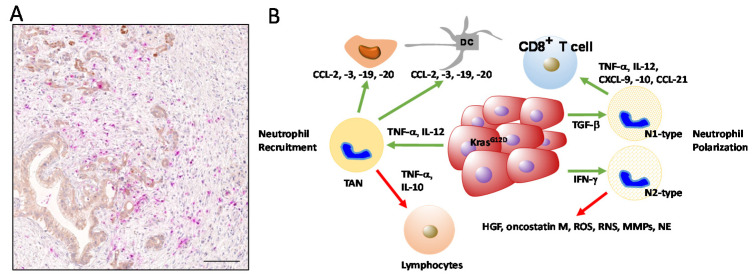
Figure 3.
Tumor-associated neutrophils in pancreatic cancer. (A) Neutrophils in PDAC tumor stroma, stained with an antibody against Myeloperoxidase (MPO, pink). Ductal structures with tumor cells are stained in brown. Scale bar: 200 µm. (B) Signaling events leading to neutrophil recruitment (left side) and neutrophil polarization (right side). Activating signals are indicated by green, and suppressing signals by red arrows. Note that neutrophils can activate macrophages and dendritic cells, while they suppress lymphocytes. When polarized, the tumor-associated neutrophil (TAN) N1 type can activate CD8-positive T cells, whereas TAN N2 secretes a cocktail of tumor-promoting factors, such as hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), matrix metalloproteinase (MMPs), and neutrophils specific protease neutrophil elastase (NE). Furthermore, TAN N2 cells can cause an increased production of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (ROS and RNS, respectively) and can cause hypoxic signaling.