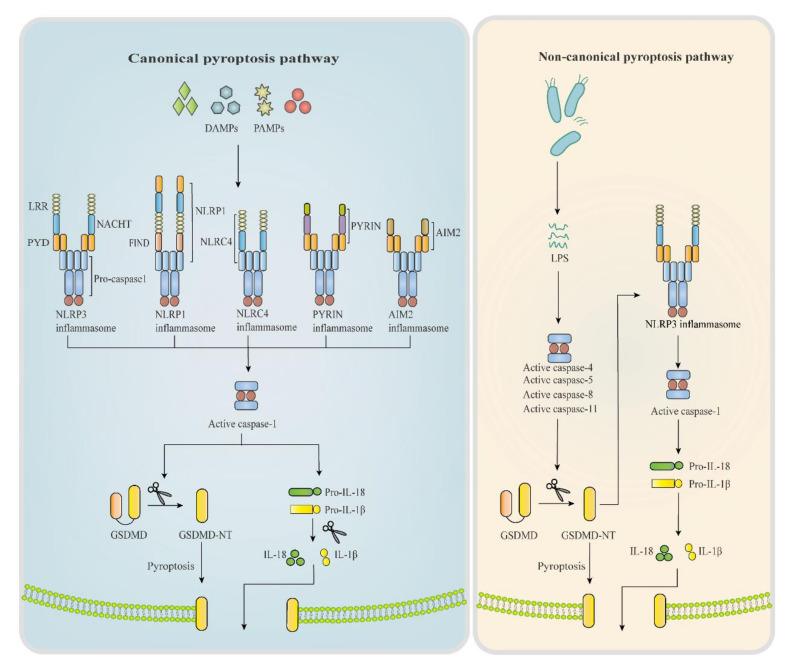
Figure 1.
Pyroptosis canonical pathway and non-canonical pathway. Working as the molecular switch of pyroptosis, inflammasomes consist of a sensor PRRs, an adaptor ASC, and an effector pro-caspase-1. During pyroptosis canonical pathway, DAMPs and PAMPs are identified by PRRs, promoting the combination of PRR’s PYD with ASC, thus recruiting pro-caspase-1 and priming complete inflammasome. Activated inflammasome triggers caspase-1 and cleaves GSDMD into GSDMD-NT, which inserts into cell membrane and resulting pore formation, accompanied by the secretion of IL-1β, IL-18. Whereas in non-canonical pathway, it’s caspase-4/5/8/11 that are activated by intracellular LPS or toxins, leading to the same cascaded reactions. PRRs, pattern recognition receptors; ASC, apoptosis-associated speck-like protein; DAMPs, damage-associated molecular patterns; PAMPs, pathogen-associated molecular patterns; GSDMD, gasderminD; LPS, lipopolysaccharides; LRR, leucine rich repeat; PYD, pyrin domain; NACTH, NACTH domain; FIND, Function-to-find domain; GSDMD-NT, GSDMD-N-terminal.